FIGURE 1.
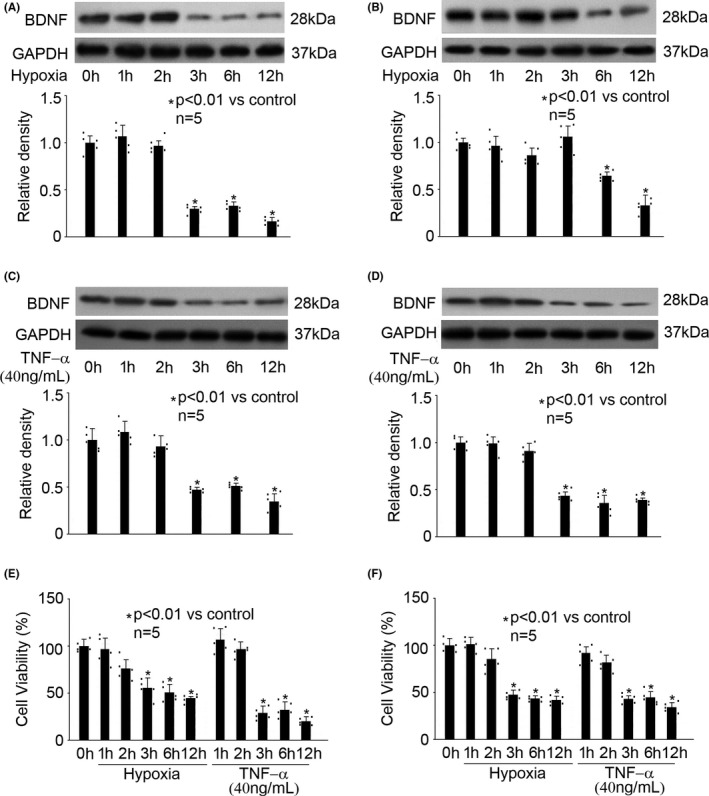
Hypoxia and TNF‐α reduced the expression of BDNF and cell viability in hippocampal neurons and astrocytes. The upper panel was a representative experiment and the lower panel was the summary of densitometric data from five separate experiments. GAPDH served as loading control. Data were expressed as normalized ratio of protein band density of BDNF against GAPDH, and were presented as mean ± standard deviation. Hypoxia treatment for 0h was considered as normoxic condition and served as control. (A) In hippocampal neurons, hypoxia reduced BDNF expression in a time‐dependent manner. (B) In astrocytes, hypoxia reduced BDNF expression in a time‐dependent manner. (C) In hippocampal neurons, TNF‐α reduced BDNF expression in a time‐dependent manner. (D) In astrocytes, TNF‐α reduced BDNF expression in a time‐dependent manner. (E) In hippocampal neurons, hypoxia and TNF‐α reduced cell viability in a time‐dependent manner. Data were expressed as the percentage of absorbance of treated cells compared with that of untreated control cells. (F) In astrocytes, hypoxia and TNF‐α reduced cell viability in a time‐dependent manner
