Figure 10.
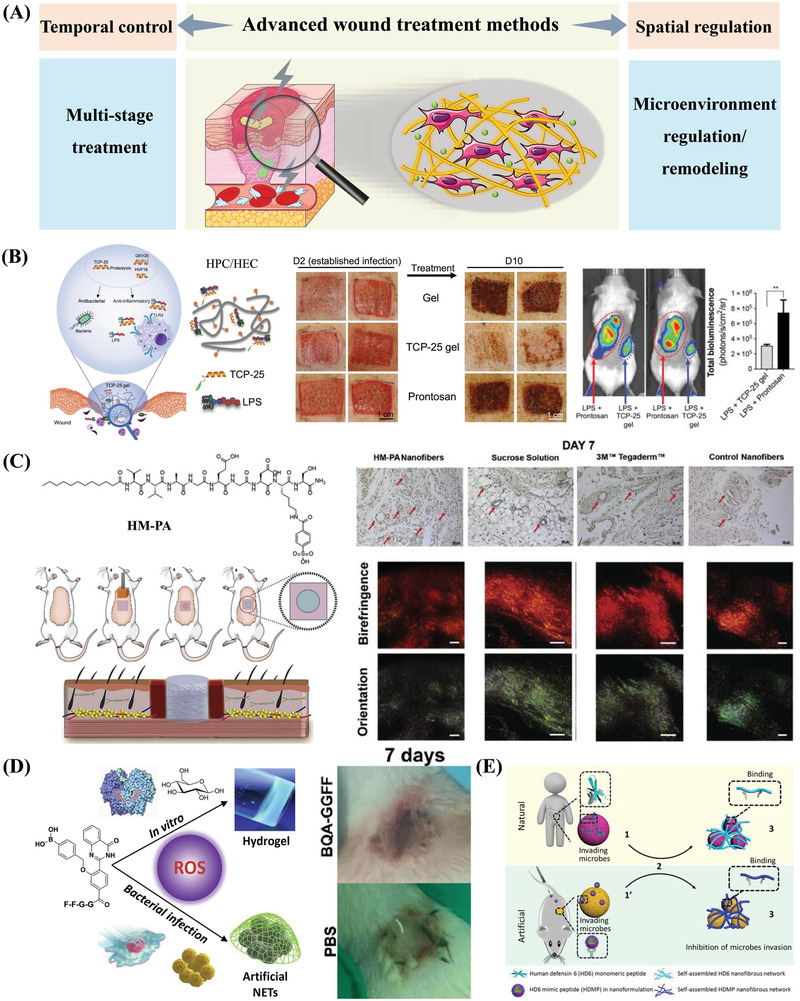
Peptide‐based self‐assembling materials for spatiotemporally controlled wound healing. A) Schematic diagram of wound treatment with spatial and temporal control. Part of the figure is modified from Servier Medical Art (http://smart.servier.com/), licensed under a Creative Common Attribution 3.0 Generic License. Multiple functions of time‐controllable peptide‐based materials for wound treatment. B) TCP‐25 hydrogel acts on wound infection and the accompanying inflammation. Photographic images of the treatment of bacterially infected mini‐pig wounds show that TCP‐25 hydrogel leads to the faster healing of infected wounds compared to common wound treatment agents. In vivo inflammation imaging also shows that TCP‐25 hydrogel has significant anti‐inflammatory activity. Reproduced with permission.[ 137 ] Copyright 2020, AAAS. C) HM‐PA hydrogel facilitates wound angiogenesis and later collagen regeneration. Staining images of blood vessels show that peptide nanofiber treatment greatly enhances angiogenesis at the wound site at day 7. Picrosirius red staining images show that peptide nanofiber scaffolds have a good wound collagen deposition ability. Reproduced with permission.[ 138 ] Copyright 2017, Elsevier Ltd. Spatially controlled regulation of the immune microenvironment by peptide‐based materials in wound therapy. D) BQA‐GGFF mimics the immune process of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) to regulate the wound microenvironment and promote wound healing. BQA‐GGFF self‐assembles into fluorescent nanofibers triggered by inflammatory ROS. Experiments using a catheter‐related infection model show that the wounds healed faster in the group treated with BQA‐GGFF compared to the PBS control. Reproduced with permission.[ 143 ] Copyright 2020, Elsevier Ltd. E) Self‐assembling cationic antimicrobial peptides mimic human defensin 6 (HD6) to trap bacteria. Schematic diagram of HDMP imitating HD6 in the human body to capture bacteria. HDMP NPs assemble into nanofibers in situ on the surface of S. aureus and trap them to inhibit bacterial invasion. Reproduced with permission.[ 145 ] Copyright 2020, AAAS.
