Figure 3.
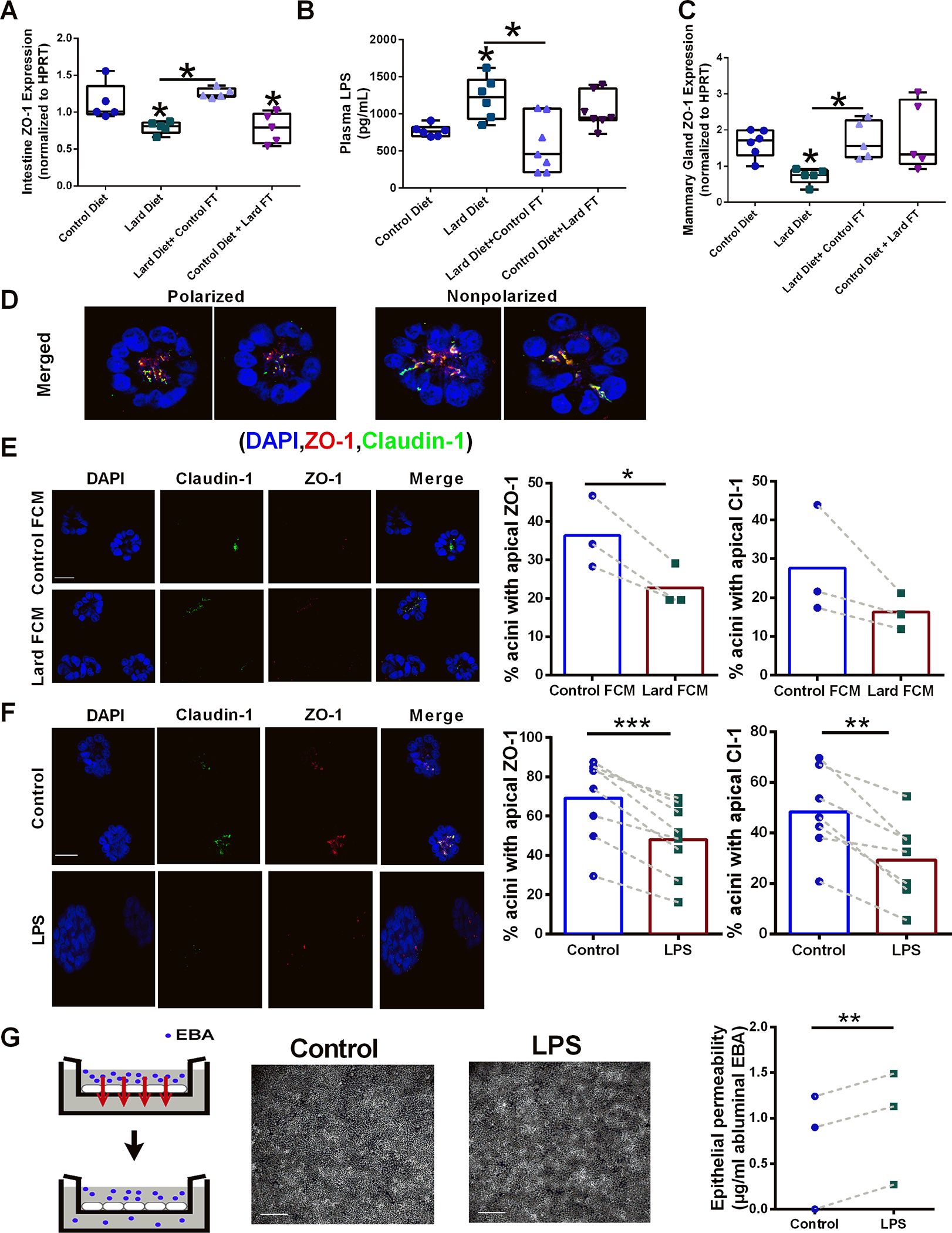
Diet-derived microbiota affects epithelial permeability and apical polarity markers. A. Relative ZO-1 gene expression normalized to HPRT in intestinal tissues from control diet-fed mice, lard diet-fed mice; lard diet-fed mice administered a control diet-derived fecal transplant, and control diet-fed mice administered a lard diet-derived fecal transplant n=5; *p<0.05. B. Circulating plasma LPS from control diet-fed mice, lard diet-fed mice, lard diet-fed mice administered a control diet-derived fecal transplant, and control diet-fed mice administered a lard diet-derived fecal transplant n=6;*p<0.05. C. Relative ZO-1 gene expression normalized to HPRT in mammary gland tissues from control diet-fed mice, lard diet-fed mice; lard diet-fed mice administered a control diet-derived fecal transplant, and control diet-fed mice administered a lard diet-derived fecal transplant n=6;*p<0.05. D. Examples of polarized and non-polarized mammary acini structures stained for the tight junction markers ZO-1 (red) and claudin-1 (green). Cell nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 10 μm. E. Mammary acini structures were treated with control diet-derived or lard diet-derived sterile conditioned media, and the effects on apical polarity were measured by ZO1 and Claudin-1 localization n=3; *p<0.05. Scale bars, 100 μm. F. Mammary acini structures were treated with PBS (control) or 1 μM LPS, and the effects on apical polarity were measured by ZO1 and Claudin-1 localization n=6;*p<0.05. Scale bars, 100 μm. G. The effect of LPS on breast epithelial permeability was measured using a transwell assay. Monolayers of breast epithelial cells were treated with PBS or LPS, and diffusion of Evans blue albumin (EBA) to the lower compartment was quantified as a measure of permeability. n=3;*p<0.05. Microscopy images of DAPI-stained nuclei show that LPS treatment did not affect cell layer confluence. Scale bars, 200 μm.
