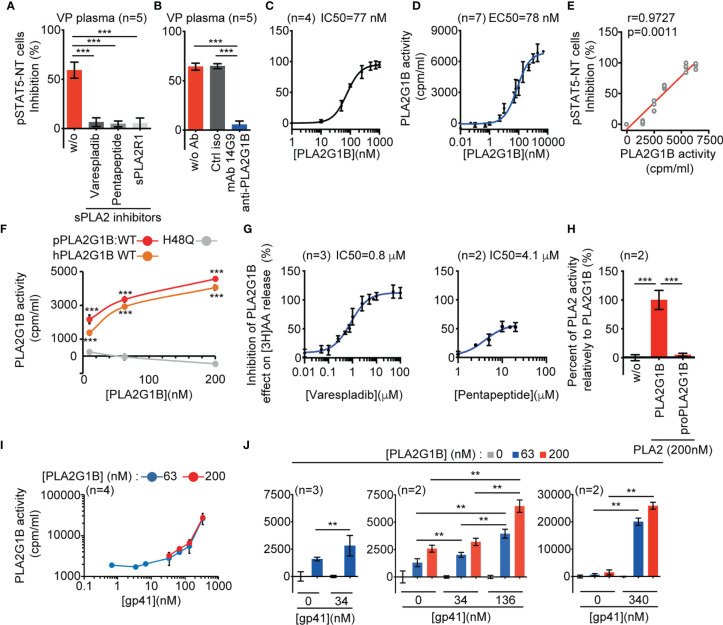
Figure 1.
HIV gp41 protein increases PLA2G1B enzymatic activity on CD4 T-cell membranes. (A, B) The sPLA2 inhibitors varespladib, pentapeptide, and sPLA2R1 and the anti-PLA2G1B mAb 14G9 strongly inhibit PLA2G1B activity in HIV viremic plasma. Purified HD CD4 T cells from two donors (A) and three donors (B) were treated with 3% of VP plasma from five viremic HIV patients together with varespladib (50 µM), pentapeptide (15 µM), sPLA2R1 (160 nM), or not (A) or control isotype (ctrl iso) or 14G9 mAb (667 nM, B) and the pSTAT5-NT cell response to IL-7 was analyzed by confocal microscopy. (C) PLA2G1B inhibits the pSTAT5-NT cell response to IL-7 in a dose-response manner. HD CD4 T cells were purified from four donors. The IC50 value is indicated. Results are shown as the mean ± SD of the percentage of pSTAT5-NT cell inhibition for A-C. (D) PLA2G1B activity can be followed in a dose-response manner on human CD4 T cells labeled with tritiated arachidonic acid. CD4 T cells purified from four donors were incubated with several concentrations of PLA2G1B (0.1 nM-5 µM) for 2 h. Then, the release of [3H]-AA in the cell supernatant due to PLA2G1B activity was quantified with a radioactivity counter (tri-Carb 2800 TR liquid scintillation analyzer, Perkin Elmer). Results are shown as the mean ± SD of PLA2G1B activity in cpm/mL from a pool of seven experiments. The EC50 value is indicated. (E) pSTAT5-NT cell inhibition positively correlates with PLA2G1B enzymatic activity on [3H]-AA-labeled CD4 T cells. Potential correlations were analyzed using the Pearson r test and a linear regression is presented. (F) [3H]-AA release is dependent on PLA2G1B enzymatic activity. [3H]-AA-labeled CD4 T cells were treated with several concentrations (10, 63, 200 nM) of WT human (hPLA2G1B) or WT or the catalytic-site mutant H48Q porcine PLA2G1B (pPLA2G1B). Results are shown as the mean of PLA2G1B activity ± SD of one experiment with the treatment in triplicate. (G) Varespladib, and pentapeptide strongly inhibit PLA2G1B enzymatic activity on [3H]-AA-labeled CD4 T cells. Results are shown as the percentage of inhibition of PLA2G1B activity on cells treated with PLA2G1B (65 nM) and several doses of inhibitors. IC50 values are presented. (H) ProPLA2G1B is inactive in the [3H]-AA release assay on CD4 T-cell membranes. [3H]-AA-labeled CD4 T cells were treated in triplicate with PLA2G1B or proPLA2G1B at 200 nM. Results are shown as the percentage of activity with proPLA2G1B relative to that of PLA2G1B. (I, J) HIV gp41 increases PLA2G1B activity in a dose-dependent manner on human CD4 T cells. [3H]-AA-labeled CD4 T cells were incubated alone or with PLA2G1B (63 nM or 200 nM) in the presence or not of several concentrations of recombinant gp41 protein (0.68 nM-340 nM). Results are shown as the mean ± SD from a pool of four experiments for I and n = 2-3 experiments for (J) **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction for multiple comparisons (A, B, F, H) and the Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by the Mann-Whitney test with p-values adjusted for multiple comparisons between groups (J). For F, only comparisons between H48Q and WT hPLA2G1B or pPLA2G1B at each PLA2G1B concentration are shown.