Fig. 6.
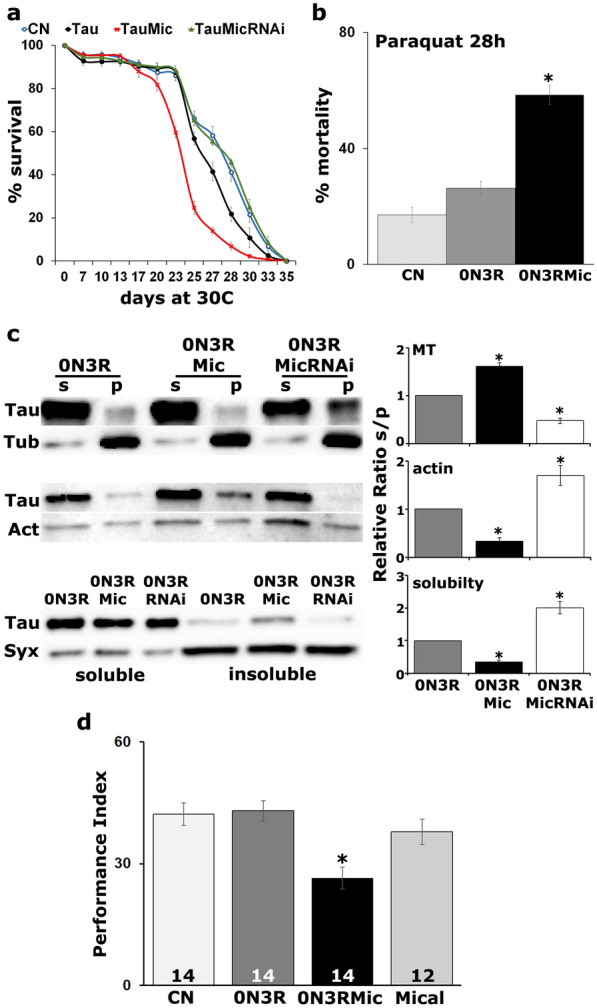
Mical equally affects the neurotoxicity of hTau0N3R isoform. a Survival curves for animals expressing panneuronally the indicated transgenes at 30 °C, in comparison with elavC155-GAL4/+;tub-Gal80ts/+ controls (CN). Statistical analysis using the log rank test indicated significant differences in longevity after accumulation of hTau0N3R alone and upon co-overexpression with Mical. b Response of flies expressing panneuronally the hTau0N3R transgene (dark grey bar) to the oxidant molecule paraquat, compared with the same transgene upon co-overexpression of Mical (black bar). Star indicates significant difference from the transgene without Mical overexpression. Control flies (CN) are driver elavC155-GAL4/+ flies (light grey bar). c Endogenous microtubules (upper panel), phalloidin-bound F-Actin (middle panel) and aqueous soluble and insoluble fractions (lower panel) were isolated from flies expressing under the elavC155-GAL4 driver the hTau0N3R transgene alone or upon Mical up and down-regulation. p: pellet and s: supernatant fractions were analyzed by western blotting using antibodies against Tau (5A6), Tubulin (E7), Actin and Syntaxin. Stars indicate significantly altered levels of precipitated 0N3R upon modulation of Mical levels compared to Tau expressed alone. d Memory performance of animals expressing panneuronally the hTau0N3R transgene (dark grey bar), compared with the same transgene upon co-expression with Mical (black bar). Control flies (light grey bars) are driver elavC155-GAL4/+ flies (CN) and flies that overexpress Mical under the panneuronal elavC155-GAL4 driver. Star indicates significant differences from both controls
