Fig. 3.
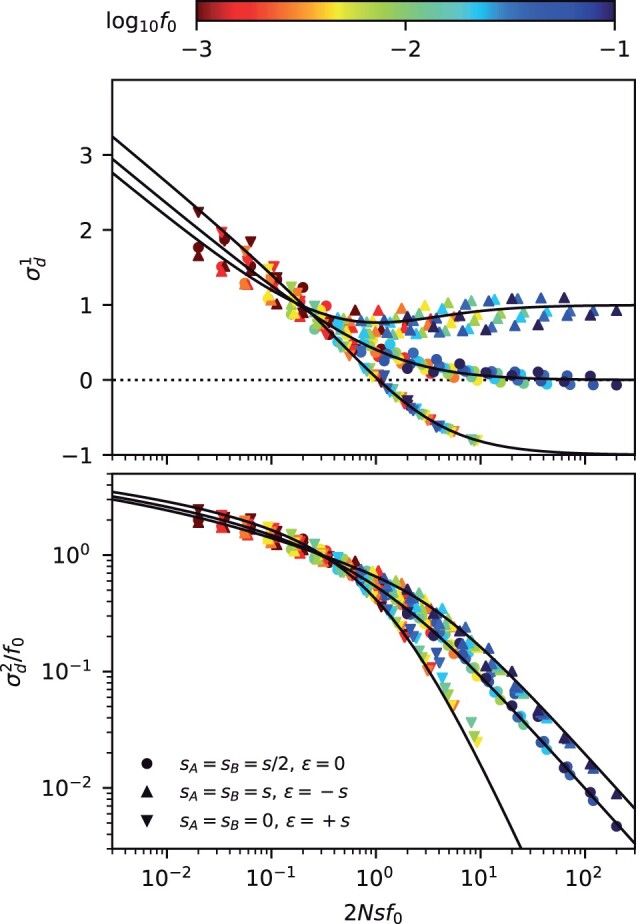
Frequency-resolved LD between deleterious mutations as a function of the scaled fitness cost of the double mutant. Top: the signed LD moment, , in Equation (7) is depicted for pairs of nonrecombining loci with additive (ϵ = 0), antagonistic (ϵ), and synergistic (ϵ) epistasis, which were chosen to have the same total cost for the double mutant (). Symbols denote the results of forward-time simulations (Appendix A) across a range of parameters with , and each symbol is colored by the corresponding value of f0. The solid lines shows the theoretical prediction from Equation (C8). Bottom: an analogous figure for the squared LD moment, , where solid lines show the theoretical predictions from Equation (C9). The “data collapse” in both panels indicates that frequency-weighted LD is primarily determined by the compound parameters and Nϵf0. Weak scaled fitness costs () lead to an excess of coupling linkage (), which qualitatively resembles the effects of antagonistic epistasis (ϵ).
