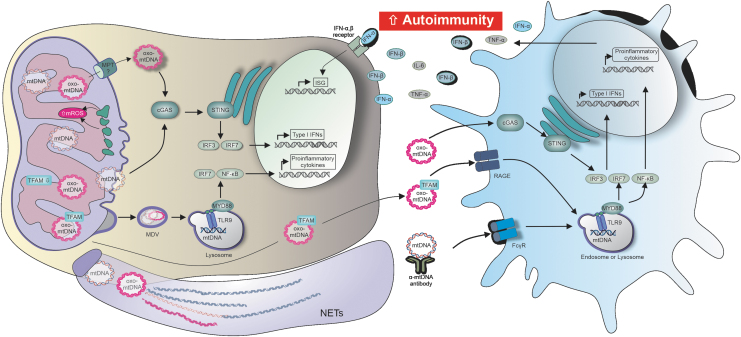
FIG. 5.
Oxidized and nonoxidized mitochondrial nucleic acids induce proinflammatory cytokine secretion, and contribute to the onset and progression of autoimmunity, through multiple distinct pathways. mtDNA and mtRNA were shown to be per se immunogenic by acting as DMAPs on multiple pathways, such as cGAS/STING or TLR-mediated signaling. Oxidized and nonoxidized mtDNA also play an important role in NETosis, and mtDNA complexed with the transcription factor TFAM showed an augmented immunogenicity. Mitochondrial nucleic acids that reach the extracellular space induce cytokine secretion in bystander cells. Systemic or chronic inflammation is induced through sustained cytokine secretion, and quite possibly a major contributing factor to the onset or progression of autoimmune diseases such as SLE. cGAMP, cyclic guanosine-adenosine-monophosphate; cGAS, cGAMP synthase; Fcγ, constant fragment gamma receptor; ISG, interferon-stimulated gene; RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation endproducts; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; TLR, Toll-like receptor.