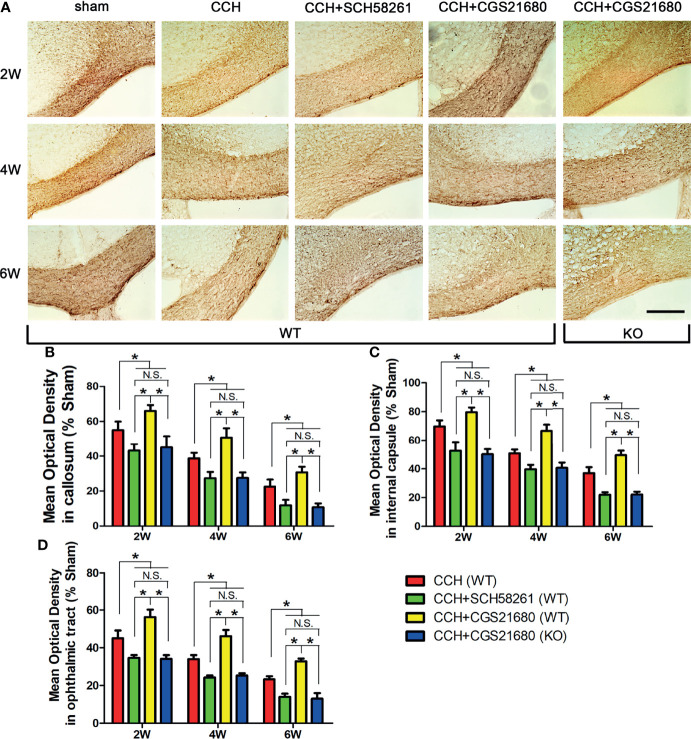
Figure 1.
Activation of ADORA2A reduced white matter injury in the mouse model of CCH induced white matter lesions. (A) Detection of white matter injury in the corpus callosum using immumohistochemical staining for MBP after CCH. (B–D) Statistical analysis of the MBP absorbance in the corpus callosum (B), internal capsule (C), and optic tract (D) at the end of 2nd, 4th, and 6th week after CCH, respectively. These results suggest that hypoperfusion leads to white matter injury in a time-dependent manner, and the activation of ADORA2A could inhibit the injury caused by CCH. Scale bars = 50 μm; N = 6; N.S. indicated no significant difference, *P < 0.05.