Photochemical modifications for DNA/RNA oligonucleotidese.
| # | Photoreaction type | Photoreactive group | Structure | Reaction wavelength (nm) | Reversible?b | T m effect | Photoreaction time scale | Nucleic acid position | Biological application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (I) Photocleavage – irreversible | o-Nitrobenzyla (& NPE, NPM, NPOM, PNVOM, NDBF, etc) |
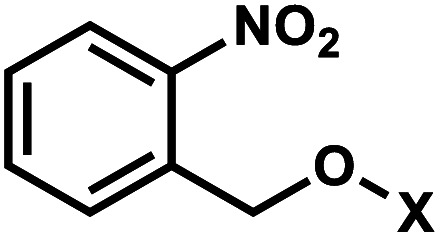
|
345–420 | No | ↓ | sec–min | Bases, backbone, ribose | Variety of biological systems (see text) |
| 2 | (I) Photocleavage – irreversible | p-Hydroxyphenacyl (& HBT) |
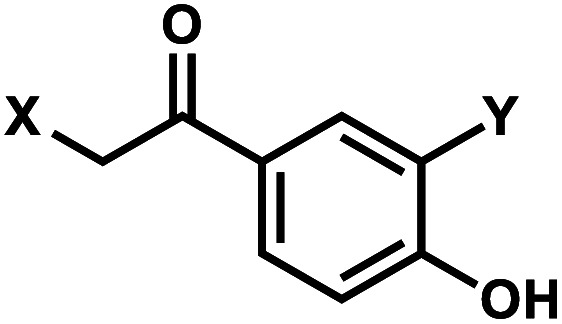
|
295–405 | No | ↓ | msec–sec | G, T bases | Control of antisense RNA annealing |
| 3 | (I) Photocleavage – irreversible | TEEP-OH |
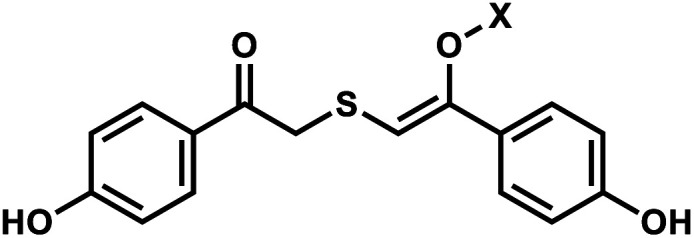
|
300–365 | No | ND | min | Phosphate backbone on DNA | Regulation of DNAzyme activity |
| 4 | (I) Photocleavage – irreversible | Aryl sulfide |

|
350 | No | ↓ | μsec–min | U, T bases | Control of RNA riboswitch folding |
| 5 | (I) Photocleavage – irreversible | Nitroindole |

|
350 | No | ↓ | min | Deoxyribose as a purine analogue | Catch and Release DNA Decoys |
| 6 | (I) Photocleavage – irreversible | Benzophenone, acetophenone |

|
365 | No | ND | min | G, C bases | Regulation of mRNA translation; photocrosslink with bound proteins |
| 7 | (I) Photocleavage – irreversible, (II) Intermolecular photocrosslinking via [2 + 2] cycloaddition – reversible | Coumarin (& DEACM, Bhc; quinoline. Cf. psoralen) |

|
350–470 | No for cleavage; Yes for crosslinking (254) | ↓ | sec–min | G, T bases, phosphate, backbone linker | Catch-and-release DNA decoy, regulation of mRNA caging, transient DNA polymerization, aptamer |
| 8 | (II) Intermolecular photocrosslinking via [2 + 2] cycloaddition – reversible | Carbazolea (&CNVK, CNVD, PCX, and PCXD) |

|
365–450 | Yes (312) | ↓↑ | sec–min | Nucleoside | RNA FISH, plasmid labeling, antisense DNA, regulation of DNAzyme activity |
| 9 | (II) Intermolecular photocrosslinking via [2 + 2] cycloaddition – reversible, (III). Cis–trans photoisomerization – reversible | Vinyl-derivative (& stilbazole, cyanostilbene, styrylpyrene; 8ST, 8NV and 8FV) |

|
340–465c, 370–420d | Yes (≤300–340c) (254–310d) | ↓↑ | min–hour | Nucleoside, G base | DNA hybridization, regulation of gene expression |
| 10 | (III) Cis–trans photoisomerization – reversible | Azobenzenea |

|
365 | Yes (400–420) | ↓↑ | sec–min | Nucleoside backbone linker, G, A bases | Variety of biological systems (see text) |
| 11 | (IV) Intramolecular photocyclization – reversible | Spiropyrans |

|
365 | Yes (400–520) | ND | min–hour | Backbone | ND |
| 12 | (IV) Intramolecular photocyclization – reversible | Diarylethene |
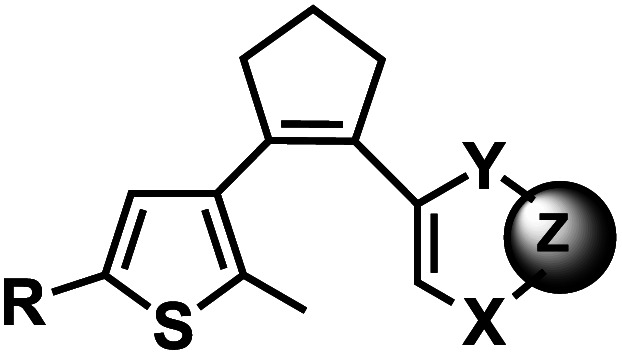
|
250–370 | Yes (>400) | ↓ | sec–min | U, C bases, A analogue (deazapurine) | ND |
Some derivatives (e.g., d-tAzo) are commercially available.
Wavelengths in parentheses indicate those for the reverse, uncrosslinking reactions.
Wavelengths for (un)crosslinking reaction.
Wavelengths for cis–trans/trans–cis isomerization.
N.B. All modifications can be incorporated in solid-phase oligonucleotide syntheses (e.g. via phosphoramidite chemistry) unless otherwise noted (e.g., DMNEC as a part of oNB, TEEP-OH, and DPMTC as a part of coumarin).
