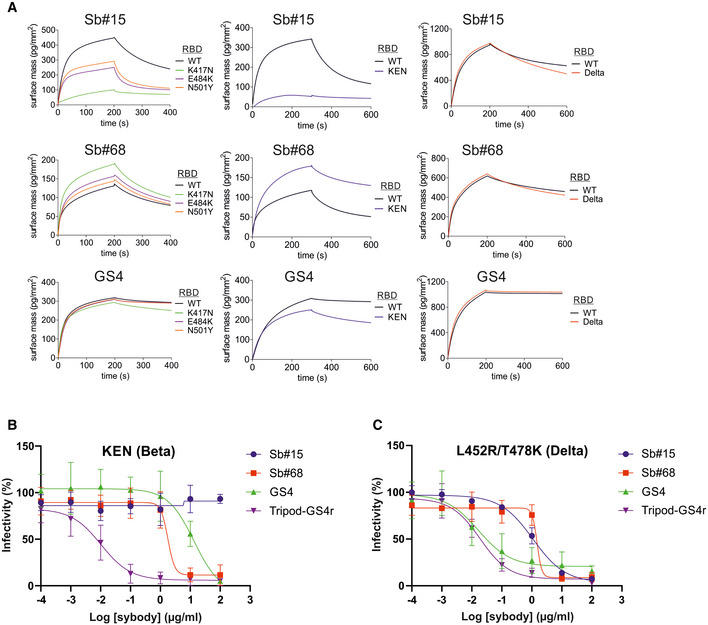
Figure 6. Affinity and neutralization by sybody constructs for variants of concern.
-
AGCI‐based kinetic analysis of interactions between immobilized sybodies (indicated above each plot) and wild‐type (WT) or mutant RBDs carrying the individual K417N, E484K, or N501Y mutations (left panels), the combined triple KEN (Beta) mutations (middle panels), or the double L452R/T478K (Delta) mutations (right panels). Sb#15, Sb#68, and GS4 were immobilized on independent flow‐cells via biotinylated Avi‐tags, and the RBD variants were sequentially injected at a concentration of 200 nM.
-
B, CNeutralization assays using VSVΔG pseudotyped with SARS‐CoV‐2 spike protein containing the triple KEN (Beta) mutations (B) or the double L452R/T478K (Delta) mutations (C). Relative infectivity in response to increasing binder concentrations was determined. Error bars correspond to standard deviations of three biological replicates.
