Fig 4. Bcl-2 antagonizes Bim to maintain survival of CD122+ IELp.
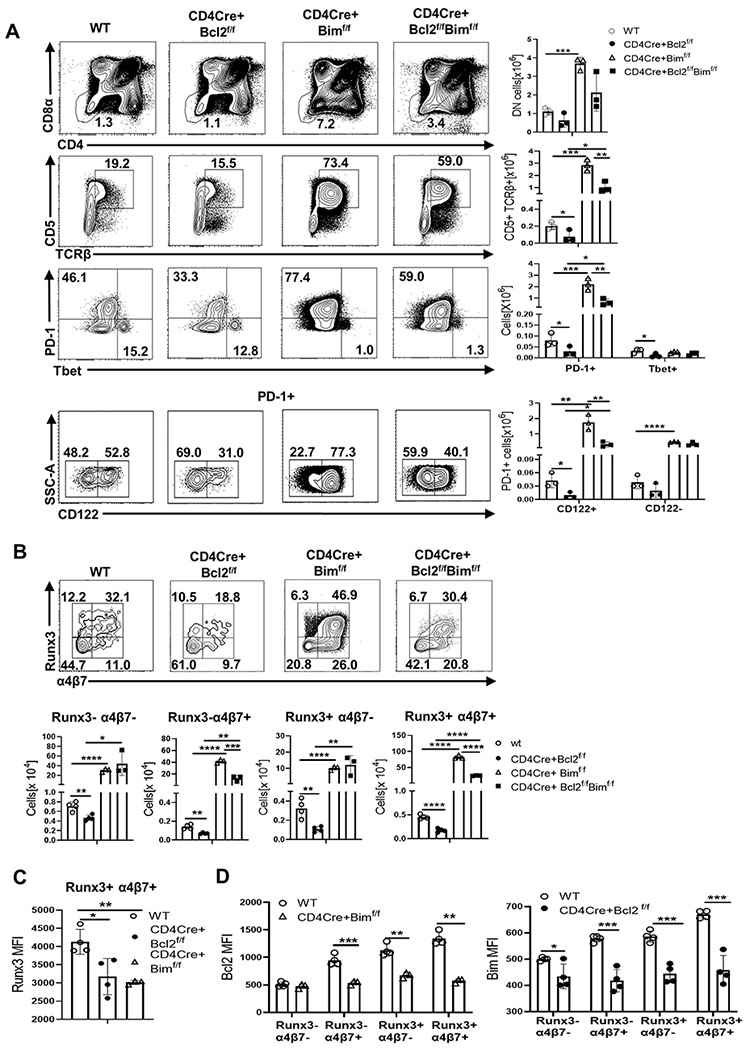
Dot plots show frequencies and bar graphs show thymocyte numbers from WT (open circle), CD4Cre+Bcl2f/f (filled circle), and CD4CreBimf/f (open triangle) and CD4CreBimf/f Bcl2f/f (filled square) mice of (A) DN (CD25− CD1tet− CD4− CD8−) (Row 1) , CD5+ TCRβ+ among DN (Row 2), PD-1+ and Tbet+ among CD5+ TCRβ+ DN (Row 3) , and CD122+ and CD122− among the PD-1+ (Row 4) (B) Runx3− α4β7− , Runx3− α4β7+ , Runx3+ α4β7− and Runx3+ α4β7+ cells within PD-1+ CD122+ CD44lo thymocytes (C) Bar graph compares MFI of Runx3 in the Runx3+ α4β7+ sub-population in WT (open circle), CD4CreBcl2f/f (filled circle), and CD4CreBimf/f (open triangle) mice. (D) Bar graphs compare MFI of Bcl-2 in Runx3− α4β7− , Runx3− α4β7+ , Runx3+ α4β7− and Runx3+ α4β7+ sub-populations between WT (open circle) and CD4CreBimf/f (filled square) mice and of Bim between WT (open circle) and CD4CreBcl2f/f (filled circle) mice. Results are representative of at least 3 independent experiments with n=3 or more mice per group and show mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 Student’s t test.
