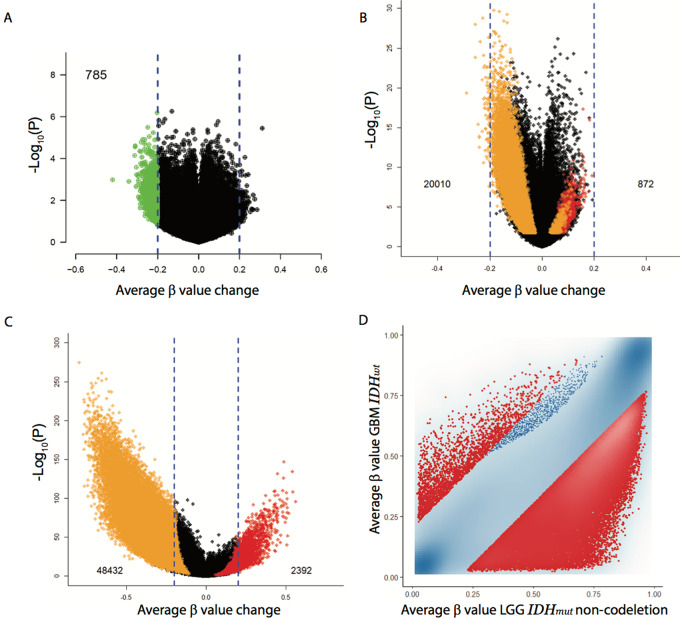
FIGURE 1.
DNA methylation changes during IDH-wild-type (IDH-wt) GBM recurrence. A, Volcano plot comparing the average methylation change from primary GBM to recurrent GBM using paired samples from TCGA and from our institutions (450K methylation platform). 785 probes with reduced methylation in recurrent GBM of >0.2 on the average beta scale are shown in green. B, Volcano plot comparing overlapping CpGs from GBM to LGG (not specific for IDH) using TCGA methylation data (450K methylation platform). Colored dots represent CpG sites that show significant hypermethylation, FDR<0.05 and Δβ > 0.2, (red dots, total count provided) or hypomethylation, FDR<0.05 and Δβ < −0.2, (orange dots, total count provided) including those that were inconsistent between the model coefficient and the Δβ direction. C, Volcano plot comparing overlapping CpGs from GBM (IDH wt) to LGG (IDH mutant). Colored dots represent as in B. D, GBM (IDH wt) –LGG (IDH mutant) scatterplot, each axis representing the average β-value per interrogated CpG, GBM IDH-wt on the y-axis and LGG IDH-mutant on the x-axis.