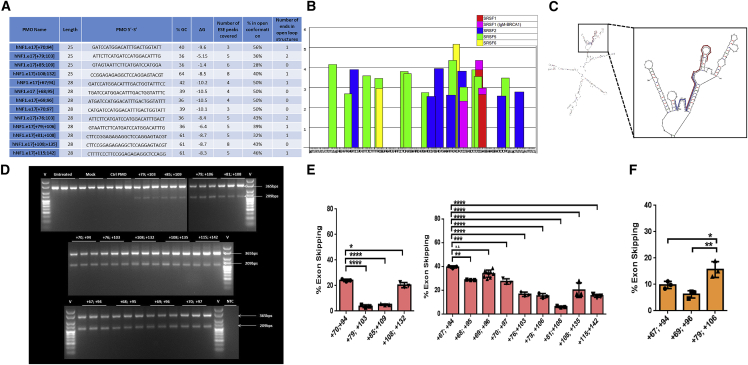
Figure 4.
Exon 17 PMO design and efficiency
(A) Table 1 summarizing designed ASO characteristics displaying percent GC content, number of ESE motifs covered, strength of binding, percent open conformation, and number of ends in open loop structures. (B) ESEfinder analysis of NF1 exon 17 with 50 nucleotides from each flanking intron. ESEfinder shows the ESE-binding motifs for indicated SR proteins that are above the threshold level in graphical format. The height of the bars indicates the motif scores generated by the tool. The width of the bar represents the length of the motif (6, 7, or 8 nucleotides). The different colors represent the different SR proteins. (C) mFold analysis of exon 17 NF1 pre-mRNA with 250 nucleotides of flanking intronic sequence, showing the most bioenergetically favorable folded structure, with two designed ASOs mapped as examples. (D and E) Gel electrophoresis and densitometric assessment of NF1 exon skipping, for four 25mer and nine 28mer ASOs with a phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) chemistry. ASOs were transfected at a 2 μM dose using 6 μM Endoporter into WT HEK293 cells, and 24 h post-treatment cDNA was generated and subjected to nested PCR. Amplicons were separated on 3% (w/v) agarose gels, yielding full-length and exon 17 skipped amplicons of 365 bp and 209 bp, respectively (representative results shown in D) and quantified using densitometric analysis using ImageJ (E). (F) The same process described was repeated for three 28mer ASOs in the A15 HEK293T culture (mutation c.1885G>A) and the exon skipping quantified.