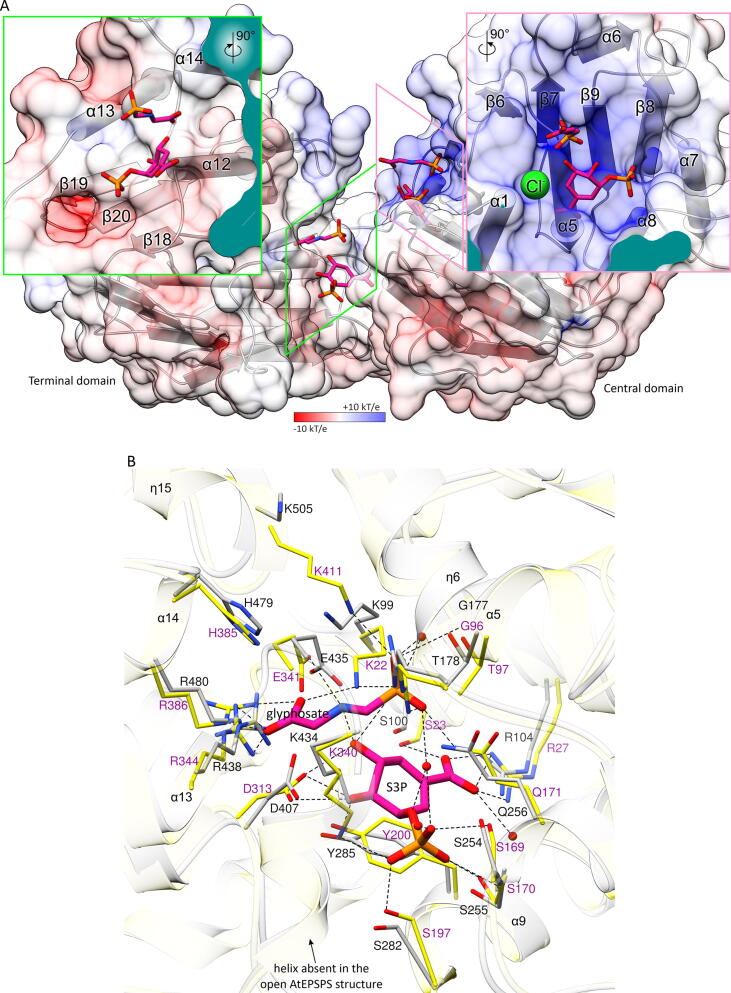
Fig. 4.
Features of the active site of AtEPSPS. Panel A presents structure in surface representation with electrostatic potential distribution according to the key (bottom). Secondary structure elements are shown as pipes and planks. Mapping of the ligand-binding surface areas onto AtEPSPS in open conformation was performed by superimposing domains of the EcEPSPS structure in complex with S3P and glyphosate (PDB ID: 1g6s [45]). This way, the binding sites were mapped independently for the terminal and central domain as illustrated in the insets. This views likely represent the in vivo scenario whereby ligand binding occurs prior to the enzyme closing. The chloride atom (green sphere) observed in the presented crystal structure is shown in the right inset. An in-depth model of the AtEPSPS active site in the closed conformation (panel B) was obtained using the AlphaFold [46] prediction of AtEPSPS (https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/P05466) that is in the closed conformation (AtEPSPS-AF, gray with black labels). AtEPSPS-AF was superposed onto the 1g6s structure (yellow with purple labels). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)