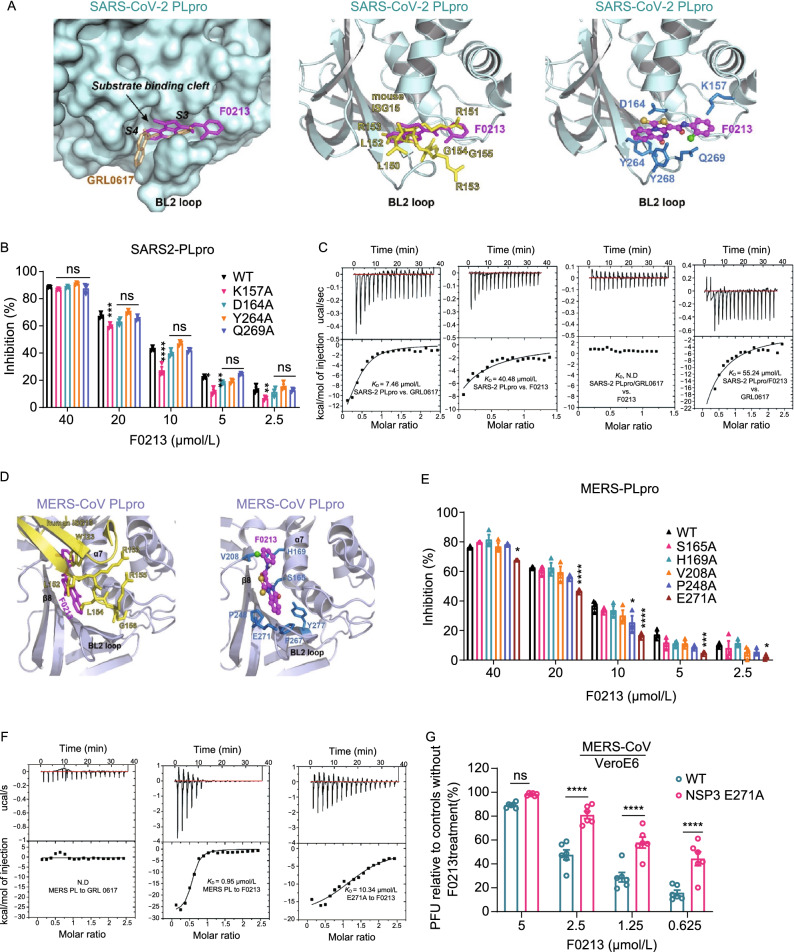
Figure 3.
Interaction between F0213 and SARS2-PLpro or MERS-PLpro. (A) Docking F0213 to SARS2-PLpro. Left, molecular surface of SARS2-PLpro (colored cyan) with GRL0617 (colored gold, PDB: 7JRN) and F0213 (colored magenta, docking model) shown in stick model. The substrate binding cleft and the BL2 loop near active site is indicated. Middle, ribbon model of SARS2-PLpro with bound mouse ISG15 (colored yellow, PDB: 6YVA). The C-terminus of mISG15 is shown with the stick model. The predicted binding mode of F0213 (magenta) is shown with stick model. Right, detailed interaction between F0213 and SARS2-PLpro; residues were predicted to interact with the inhibitor are shown with the stick models (blue). (B) In vitro inhibition of WT and mutant SARS2-PLpro by F0213. Fixed concentration of PLpro (0.1 µmol/L) and 5 µmol/L of RLRGG-AMC substrate were incubated with serial-diluted F0213. Two-way ANOVA when compared with the WT % inhibition of in each F0213 concentration. (C) Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) experiments for the binding between SARS2-PLpro and inhibitors as indicated. Disassociation constant KD is indicated; N.D. stands for non-detectable. (D) Docking F0213 to MERS- PLpro. Left, ribbon model of MERS-PLpro (colored light blue) bound by human ISG15 (colored yellow, PDB: 6BI8) is overlaid with the predicted binding mode of F0213 (colored magenta). The BL2 loop is indicated. Right, detailed interaction between F0213 and MERS-CoV PLpro; residues that were predicted to interact with the inhibitor are shown with the stick models and colored blue. (E) In vitro inhibition of WT and mutant MERS-PLpro by F0213. Two-way ANOVA when compared with the WT % inhibition of in each F0213 concentration. (F) ITC experiments for the binding between MERS-PLpro (WT or mutant) and inhibitors as indicated. Disassociation constant KD is indicated; N.D. stands for non-detectable. (G) Recombinant virus carrying the E271A substitution in MERS-CoV NSP3 confers resistance to F0213. VeroE6 cells were infected with wild-type or mutant MERS-CoV generated by reverse genetics. Antiviral activities were determined by plaque assay detecting the live virus particle in the supernatant. Results are shown as the ratio between F0123-treated and vehicle treated groups that were infected by the same virus. Two-way ANOVA. For all statistical analysis, ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01,*P < 0.05