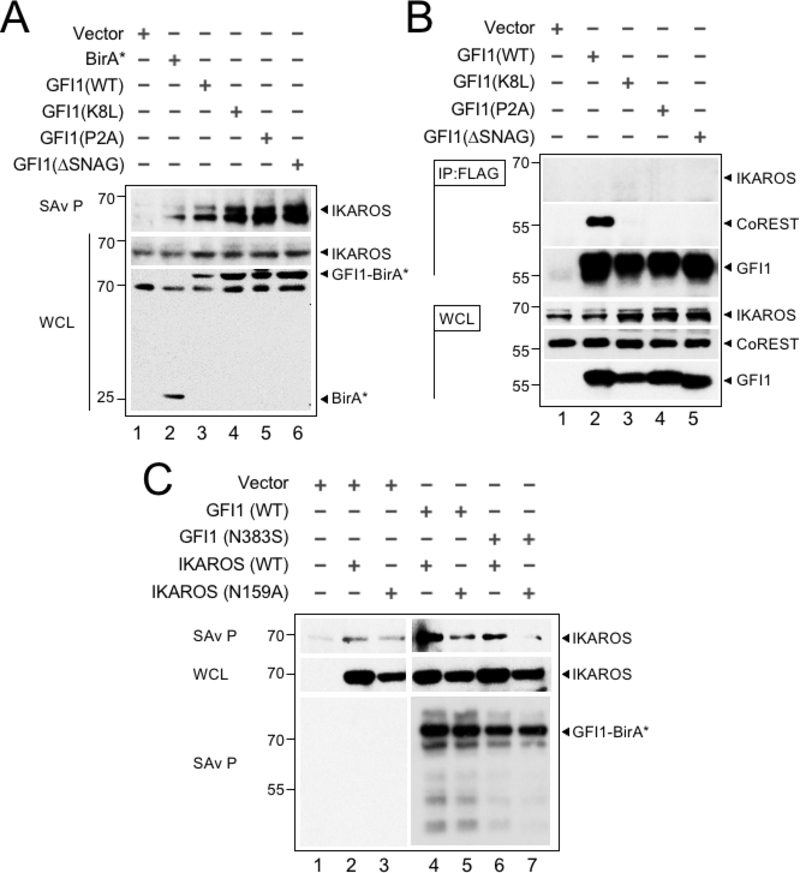
Figure 3.
The GFI1—IKAROS interaction requires DNA binding. (A) Validation and non-LSD1 binding dependence of the GFI—IKAROS proximity relationship. Biotinylated proteins in whole cell lysates from CCRF-CEM cells transduced with the indicated constructs and treated as in Figure 1B were isolated with streptavidin beads and immunoblotted with anti-IKAROS and anti-HA antibodies targeting the epitope tag in GFI1-BirA* fusion protein variants. (B) GFI1—IKAROS binding is not observed in traditional coprecipitation methods. Lysates from CCRF-CEM cells inducibly expressing wild type GFI1–3×FLAG or variants (K8L,P2A and ΔSNAG) were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody and Protein G-Sepharose. The presence or absence of IKAROS, CoREST, or GFI1 in the precipitate was detected by immunoblotting with anti-IKAROS, anti-CoREST or anti-FLAG antibodies. 2% input whole cell lysate (WCL) is shown as a control. (C) The proximity relationship between GFI1 and IKAROS requires DNA binding activity of both proteins. HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with empty vector or GFI1-BirA*-HA (wild type or N383S) together with human IKAROS-3×FLAG (wild type or N159A) expression constructs. IKAROS and control GFI1 biotinylation was monitored by precipitation with streptavidin beads and IKAROS immunoblotting as described in panel A. A GFI1 immunoblot is shown to confirm equivalent precipitation with streptavidin-Sepharose beads.