Figure 4: Effect of J007-.
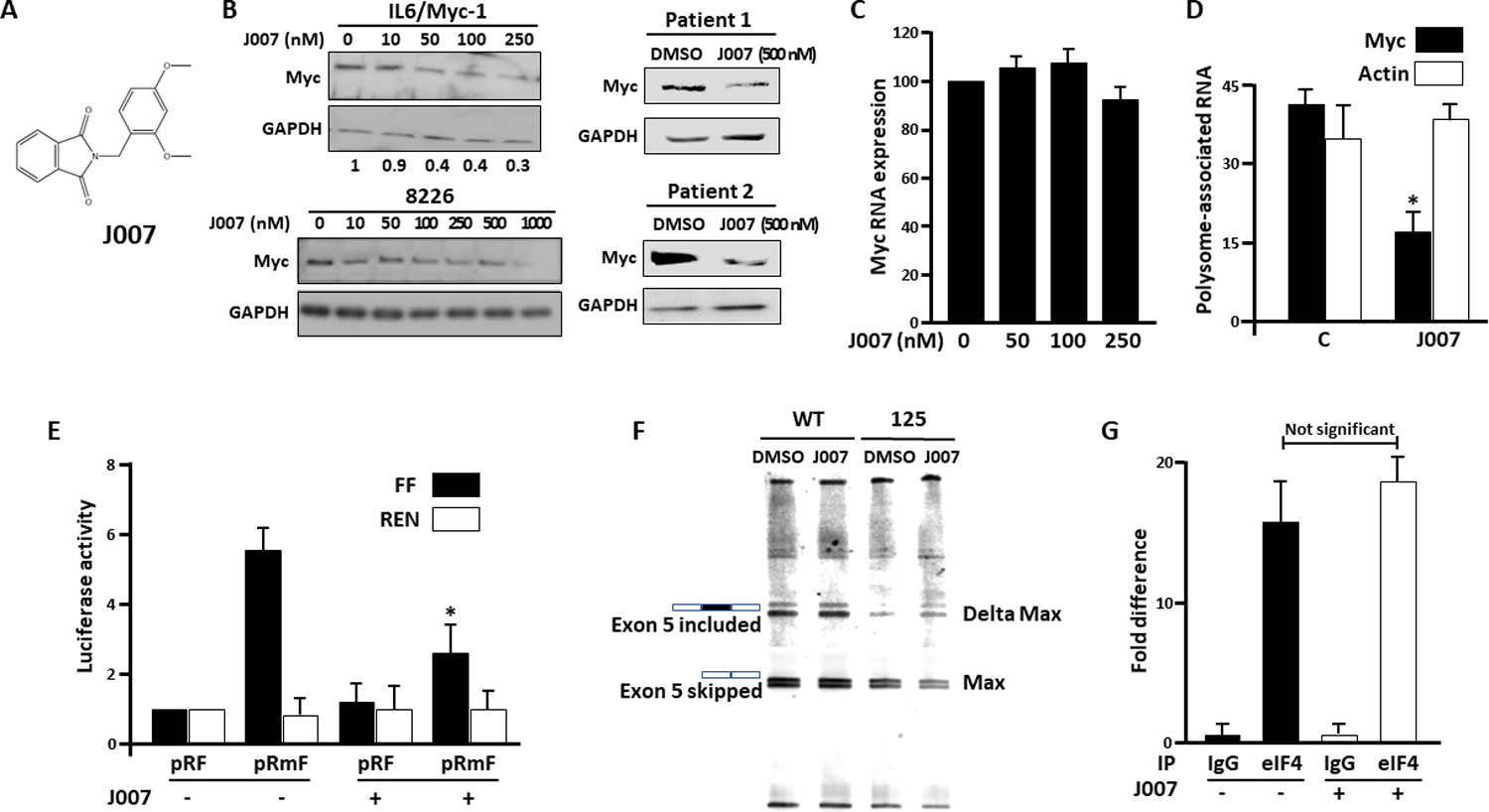
A) Structure of J007; B) Immunoblot of murine IL6/Myc-1, RPMI8226 or patient MM cells after exposure to J007 for 24 hours. IL6/Myc-1, RPMI8226 and primary cell viabilities were maintained >85% after exposure; Below IL6/Myc-1 blot are relative myc/GAPDH expression levels from 3 experiments (means); C) Relative myc RNA expression (percent of control (J007=0)) in cells exposed to J007 for 24 hours (mean+/−SD, n=3); D) Translational efficiency in cells treated +/− J007 (100nM), mean+/−SD, n=3; *=significantly (p<0.05) decreased versus control. E) Dicistronic reporter assay in cells treated +/− J007 (at 100nM) for 24 hours. Data are mean+/−SD, n=3. *= different from untreated cells, p<0.05. F) Wild type (WT) or A1-deleted 125 cells were treated +/− J007 at 100 nM and splicing analysis for Max exon 5 was performed; G) Wild type cells treated +/− J007 (100 nM for 24 hrs) were lysed and immunoprecipitated (IP) using either eIF-4E or control IgG antibody. Bound c-myc RNA was detected via qt-PCR. Data represent bound myc RNA (mean+/−SD, n=3) versus background amount in IgG control immunoprecipitates (arbitrarily designated ‘1’).
