Figure 3.
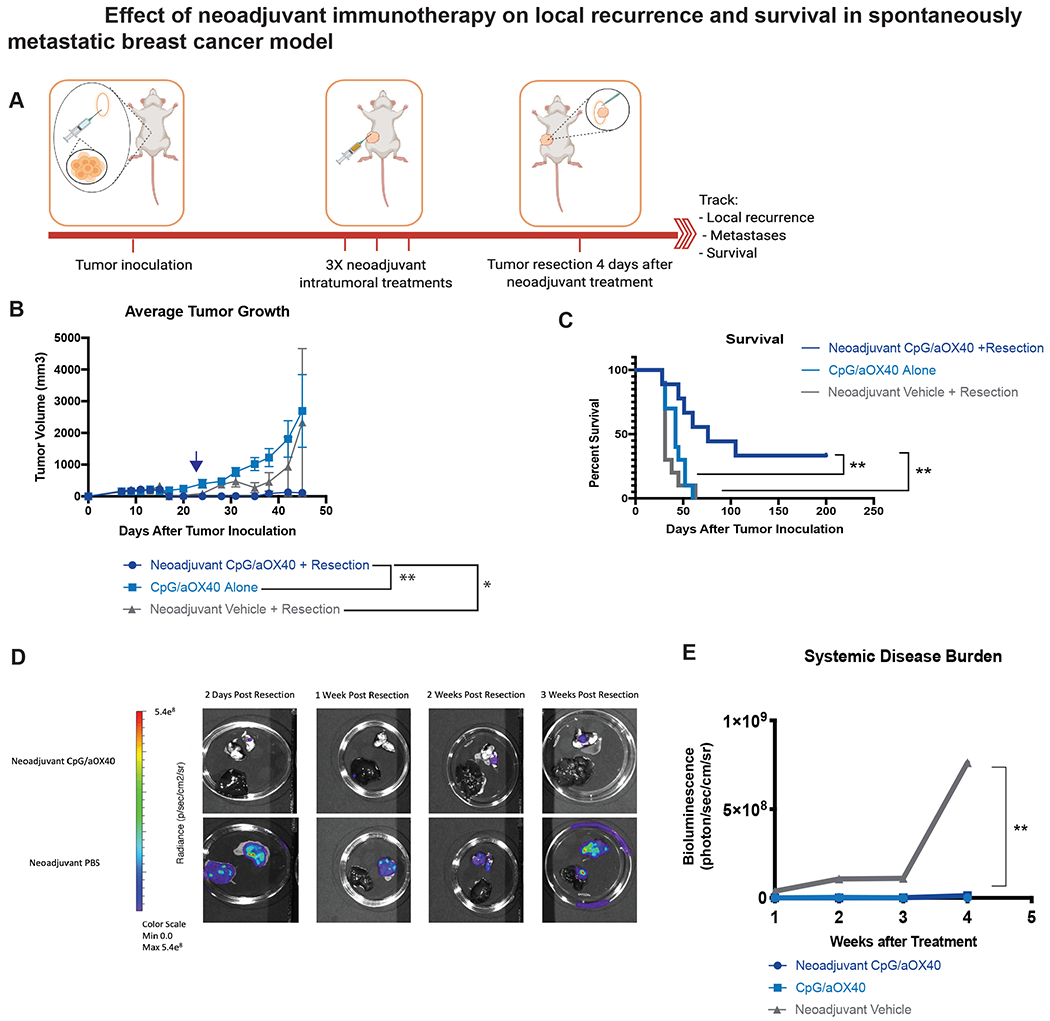
Neoadjuvant immunotherapy decreases local recurrence and improves survival in aggressively metastatic 4T1-Luc tumor model. A-C, Groups of BALB/c WT mice (n = 10) were inoculated with 7.5x104 mammary carcinoma 4T1-Luc tumor cells orthotopically into the right mammary fat pad. Groups of mice were treated with local administration of neoadjuvant immunotherapy (3X injections, 50ug CpG and 8ug aOX40 antibody per injection), immunotherapy alone (3X injections of 50ug of CpG and 8ug of aOX40 antibody per injection), or neoadjuvant vehicle. Treatment started once local (subcutaneous) tumor reached 0.7cm in diameter. Groups that underwent resection did so on day 15 (blue arrow) following subcutaneous tumor inoculation. A. Schematic illustrating experimental setup. B. Average local tumor growth in different treatment groups. Date of resection indicated by blue arrow. Data presented as mean tumor size +/− SEM. Differences in primary tumor growth between neoadjuvant vehicle followed by resection, CpG/aOX40 without resection and neoadjuvant CpG/aOX40 followed by resection were significant by unpaired t test. p = 0.008 (Neoadjuvant CpG/aOX40 + Resection vs CpG/aOX40 Alone). p = 0.04 (Neoadjuvant CpG/aOX40 + Resection vs Neoadjuvant Vehicle + Resection). C. Kaplan-Meier curves for overall survival of each group shown. P values were calculated using the log-rank test (Mantel-Cox). p = 0.006 (Neoadjuvant CpG/aOX40 + Resection vs CpG/aOX40 Alone). p = 0.002 (Neoadjuvant CpG/aOX40 + Resection vs Neoadjuvant Vehicle + Resection).
D-E. In a separate experiment, groups of BALB/c WT mice were inoculated with tumors as described above in A (n = 10). Mice from each group were euthanized at specific time points (2 days post resection, 1 week post resection, 2 weeks post resection and 3 weeks post resection) and their lungs and liver imaged ex vivo to evaluate systemic disease burden (n = 2 at each time point). The differences between the groups were statistically significant, p = 0.09 between neoadjuvant CpG/aOX40 vs Neoadjuvant Vehicle + Resection by paired t test.
