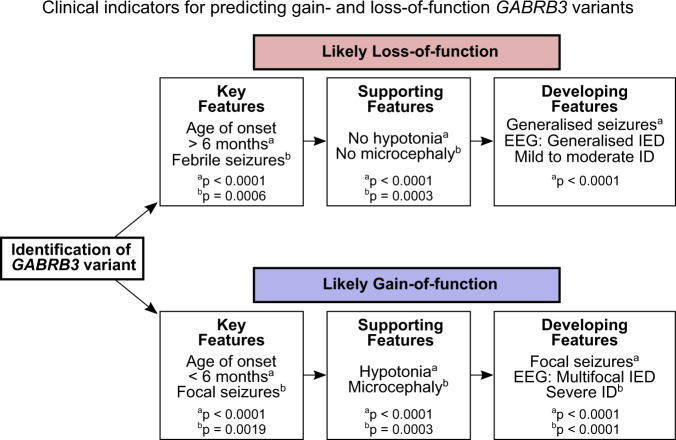
Fig. 8. Flowchart for predicting LOF and GOF GABRB3 variants based on clinical indicators.
When a GABRB3 missense variant is identified, there are several clinical features that can help predict whether the variant is LOF or GOF. Key features of LOF variants include an age of onset of 6 months or older and the presence of febrile seizures. Supporting features include a lack of hypotonia and microcephaly. As patients develop, LOF variants typically result in generalised seizures (includes atonic, myoclonic and bilateral tonic-to-clonic seizures), EEG with generalised interictal epileptiform discharges (IEDs) and ID in the normal or mild to moderate spectrum. For GOF variants, key features are focal seizures that present at an age of onset less than 6 months, and supporting features include hypotonia and microcephaly. As the patient ages, GOF variants feature focal seizures, EEG with multifocal interictal epileptiform discharges, and severe ID. If the patient presentation has a mixture of these indications, functional testing of the variant is needed to determine whether it has LOF or GOF traits. p-values comparing the clinical indicators for patients with LOF and GOF variants are included (also see Fig. 4).