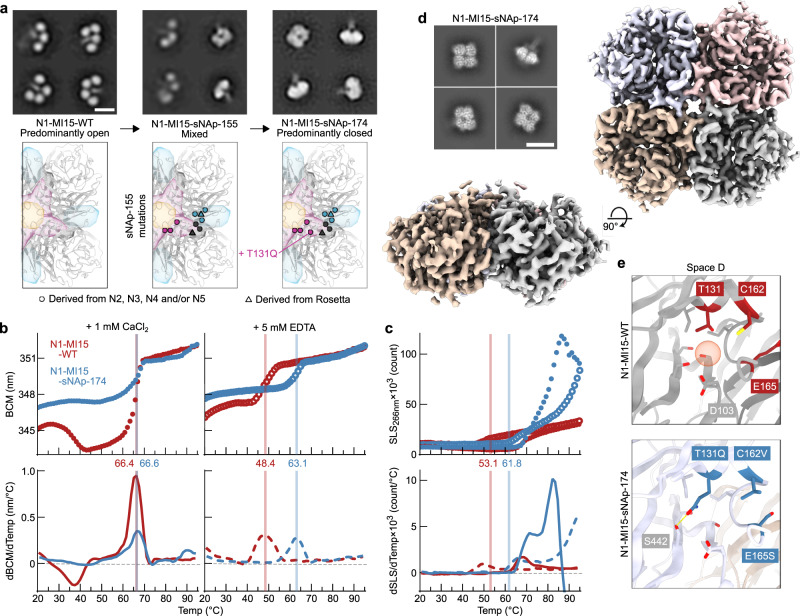
Fig. 5. Design and Structural Characterization of N1-MI15-sNAp-174.
a Application of sNAp-155 mutations to N1 MI15 and addition of the space D stabilizing mutation T131Q resulted in fully closed N1-MI15-sNAp-174 tetramers (scale bar, 10 nm). NS-EM was performed and analyzed multiple times and representative images are shown. b Thermal denaturation of N1-MI15-WT and N1-MI15-sNAp-174 in the presence of 1 mM CaCl2 (closed circles and solid lines) or 5 mM EDTA (open circles and dashed lines), monitored by intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence. Top panels show raw data, while lower panels show smoothed first derivatives used to calculate melting temperatures. The barycentric mean (BCM) of the fluorescence emission spectra is plotted. c SLS during thermal denaturation of N1-MI15-WT and N1-MI15-sNAp-174 in the presence of 1 mM CaCl2 or 5 mM EDTA, with aggregation temperatures shown for CaCl2-treated samples. Data are plotted as in panel B. d Representative 2D class averages (scale bar, 10 nm) (top left) and final 3D density (bottom left and right) from cryo-EM of N1-MI15-sNAp-174. e Space D cavity in N1-MI15-WT (top; from PDB ID 4B7Q) and N1-MI15-sNAp-174 (bottom; cryo-EM reconstruction), with the cavity marked by a red sphere. All residues shown as sticks in the WT model are conserved between N1-CA09-WT and N1-MI15-WT.