FIGURE 4.
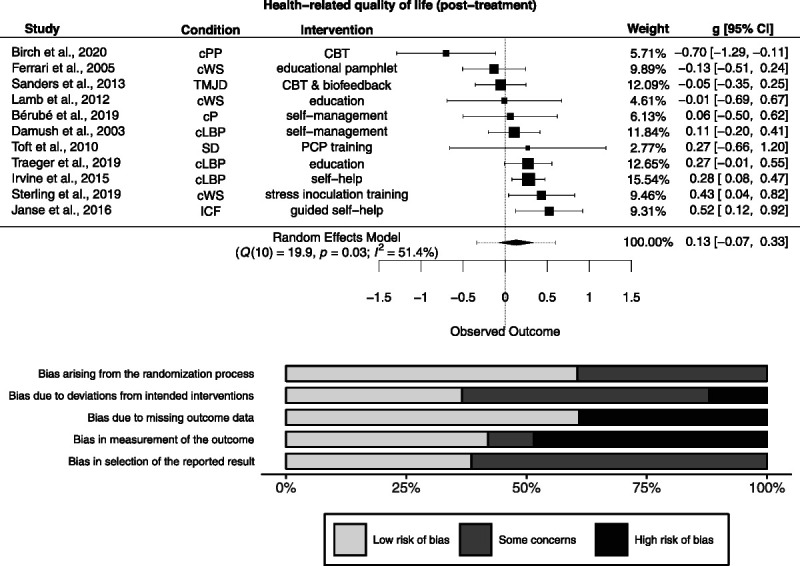
Forest plot and risk of bias inherent in the summary effect for health-related quality of life (post-treatment). g > 0 indicates more favorable outcomes in the intervention group. CBT = cognitive-behavioral therapy; cLBP = chronic low back pain; cP = chronic pain; cPP = chronic postoperative pain; cWS = chronic whiplash syndrome; ICF = idiopathic chronic fatigue; PCP = primary care physician; SD = somatoform disorder; TMJD = temporomandibular joint disorder. Study-level biases are weighted according to the meta-analytic weights. Two cluster-randomized studies were included in this meta-analysis (59,60). Whereas the study by Lamb et al. (60) was at low risk of bias arising from the timing of identification and recruitment of individual participants in relation to timing of randomization, the study by Toft et al. (59) was at high risk (not depicted).
