TABLE 4.
Meta‐analysis of the mean differences (95% CI) in change over time among VITAL‐Cog participants (n = 3424) and CTSC‐Cog participants (n = 794), by N‐3 supplement assignment
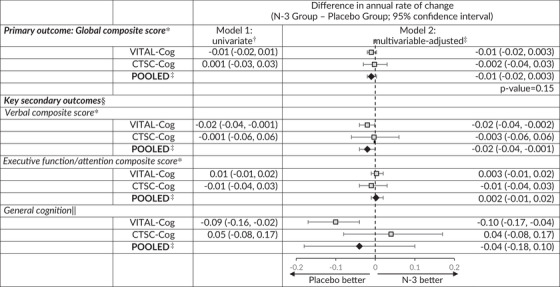
|
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; 3MS, Modified Mini‐Mental State Examination (range = 0–100); CI, confidence interval; CTSC, Clinical and Translational Science Center for VITAL in Boston, MA; TICS, Telephone Interview of Cognitive Status (range = 0‐41); 19 VITAL, Vitamin D and Omega‐3 Trial.
For definitions of the global scores and the key secondary outcomes for the two populations, see footnotes for Tables 2.
From linear mixed models of cognitive performance: model 1 includes time since randomization modeled as a continuous variable, omega‐3 assignment, and their interaction.
From linear mixed models of cognitive performance: model 2 is model 1 with adjustment for vitamin D assignment (yes/no), sex (male/female), age at randomization (years), race/ethnicity (non‐Hispanic White, Black, other), education (high school or under, college, graduate school), history of depression (yes/no; see footnote in Table 1 for definition). Pooled using Dersimonian and Laird 32 fixed‐effects method for meta‐analysis except for general cognition where the P for heterogeneity across the two substudies was 0.04 and results were meta‐analyzed with random effects.
For secondary outcomes, none of the differences in the annual rate of change were significant at the significance threshold of 0.0167 (raw P‐values ≥.04; based on Bonferroni correction of doing three simultaneous tests for the three secondary outcomes: 0.05/3 = 0.0167).
Due to the differences in scale between the TICS (0–41) used in VITAL‐Cog and 3MS (range 0–100) used in CTSC‐Cog, for pooling purposes, the 3MS scores were multiplied by 0.41 for conversion to the same scale as the TICS scores. As the P for heterogeneity across the two substudies was 0.04, the results were meta‐analyzed with the Dersimonian and Laird 32 method incorporating random effects.
