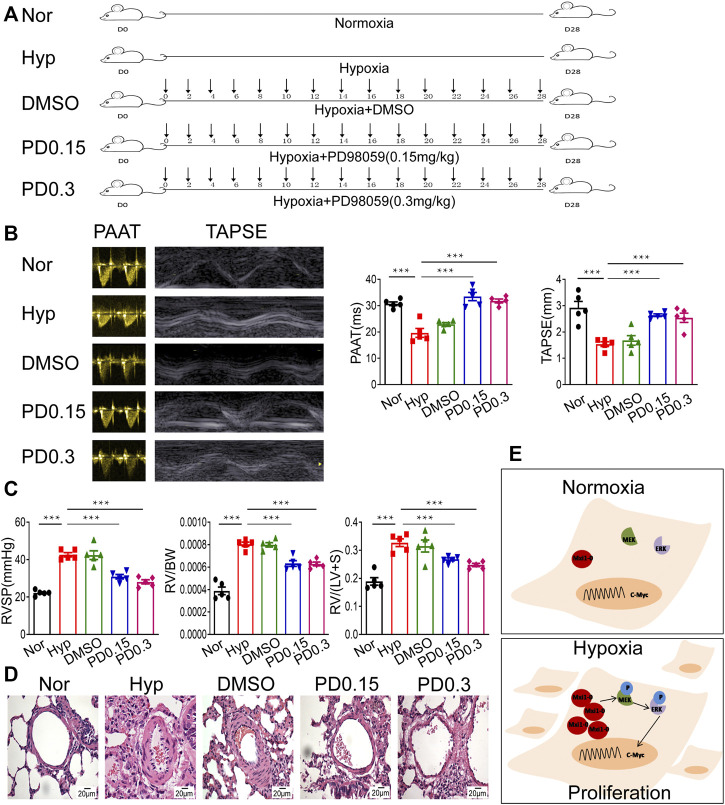
FIGURE 7.
Inhibition of MEK/ERK signaling protects rats against HPH. (A) A rat model of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension (HPH) was generated (n = 5 animals per group). Rats exposed to chronic hypoxia were treated with vehicle (DMSO) or 0.15 mg/kg or 0.3 mg/kg PD98059. (B) Rats in all groups were subjected to echocardiography and measurement of PAATand TAPSE. (C) After intubation for rats described in (A), RVSP was recorded, and the right ventricular hypertrophy ratio of RV/BW and RV/LV + S were calculated. (D) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of paraffin-fixed lung sections prepared from rats described in (A) was performed for morphological analysis of the pulmonary arteries. (E) A diagram showing that hypoxia-induced Mxi1-0 promotes PASMCs proliferation via MEK/ERK/c-Myc signaling in the context of HPH. Scale bar, 20 μm. Data are shown as means ± SDs. For statistical significance, ***represents p < 0.001 compared to hypoxia. PAAT, pulmonary artery acceleration time; TAPSE, tricuspid annulusplain systolic excursion; RVSP, right ventricular systolic pressure; RV, right ventricle; BW, body weight; LV + S, left ventricle plus septum.