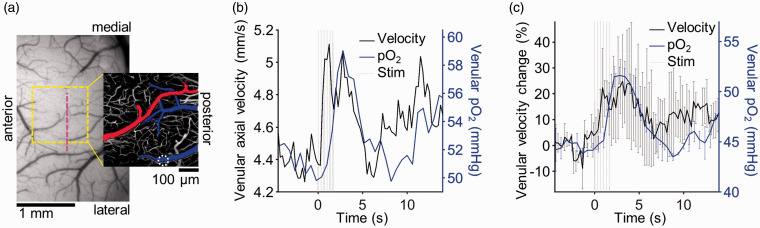
Figure 6.
Simultaneous pO2 and blood velocity measurements. (a) A CCD image of the cortical surface as seen through the chronic glass-sealed cranial window. The ROI selected for 2PM (for pO2 measurements) is marked with a yellow square. Vertical dashed line marks the position of the Doppler OCT B-scan, used to measure the axial component of the blood velocity. The pial vessels are pseudo-colored (arterioles—red; venules—blue) on the maximum intensity projection of the 2PM angiogram, encompassing ∼40 µm depth. The white dashed circle marks the location of the surfacing venule from which simultaneous absolute pO2 and velocity measurements are reported in (b). (c) Comparison between the percent change in axial component of the venular blood flow velocity and venular pO2 during functional activation (n = 2). Error bars in (c) show the velocity projection standard deviation across animals. pO2: partial pressure of O2.