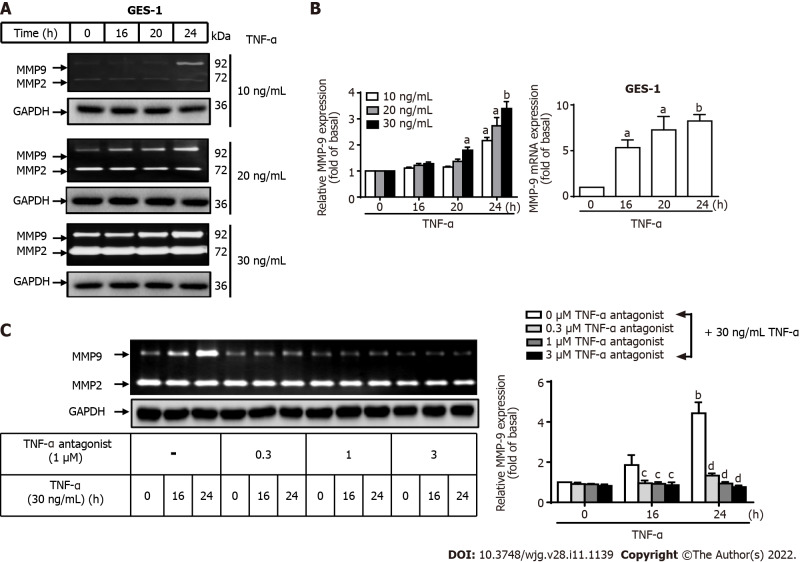
Figure 2.
Tumor necrosis factor-α induces matrix metallopeptidase-9 expression via tumor necrosis factor-α receptor in normal human gastric mucosa epithelial cells. A: Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) was used at concentrations of 10, 20, and 30 ng/mL to stimulate normal human gastric mucosa epithelial cells (GES-1) for 0, 16, 20, or 24 h, and matrix metallopeptidase-9 (MMP-9) enzymatic activity was measured by gelatin zymography as described in the Materials and Methods section; B: MMP-9 transcripts were analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; C: Cells were either untreated or treated with a TNF-α antagonist (TNFR inhibitor) (1 mM) 1 h before the addition of TNF-α (30 ng/mL). The TNF-α antagonist repressed TNF-α-activated MMP-9 expression in GES-1 cells. One-way ANOVA was used for comparisons among different treatment time points (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control cells in 0 h). One-way ANOVA was used for comparisons among different treatments (cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs TNF-α-stimulated cells). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GES-1: Normal human gastric mucosa epithelial cell line; MMP: Matrix metallopeptidase; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.