FIGURE 6.
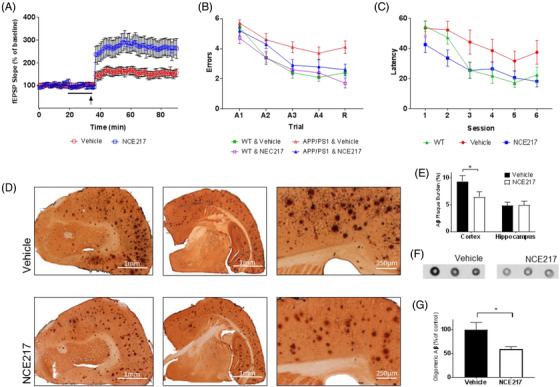
In vivo efficacy of tryptophan‐based anti‐Alzheimer's disease (AD) therapeutic compound. (A) Long‐term potentiation is strengthened in APP/PS1 transgenic murine hippocampal slices (400 μm) upon exposure to 50 μM of NCE217 (indicated by arrow)—as evidenced by heightened field excitatory postsynaptic potential (fEPSP) slope upon θ‐burst stimulation (P < 0.01). (B) In radial arm water maze testing, APP/PS1 transgenic mice treated with NCE217 (20mg/kg/day) made statistically fewer errors than mice treated with a vehicle (P = 0.04). Performance during retention (R) proved comparable to wild‐type (WT) mice, suggesting possible preservation of memory in APP/PS1 murine models. (C) In Morris water maze testing, APP/PS1 murine models treated with NCE217 (20mg/kg/day) exhibited a lower latency (time to locate a hidden platform) than vehicle‐treated models. Performance was again comparable to WT mice, suggesting possible preservation of memory (P < 0.01). (D) Amyloid beta (Aβ) plaque burden in brains of APP/PS1 mice treated with vehicle (top) and NCE217 (bottom). Plaque burden is visibly diminished with administration of NCE217, across rostral coronal sections (left), coronal sections near bregma (center), and in the cerebral cortex (right). E, Computational plaque quantification (by ImageJ software) observed significant reduction (*P = 0.024) of amyloid plaques in the cortex. F, Immunohistochemistry of Aβ in the brain, assayed by dot blots using the A11 anti‐oligomeric Aβ antibody, revealed a lower preponderance of neurotoxic oligomers in the brain upon NCE217 treatment. G, Quantification (by ImageJ) revealed a statistically significant decrease in the prevalence of oligomers (P = 0.04)
