Figure 8.
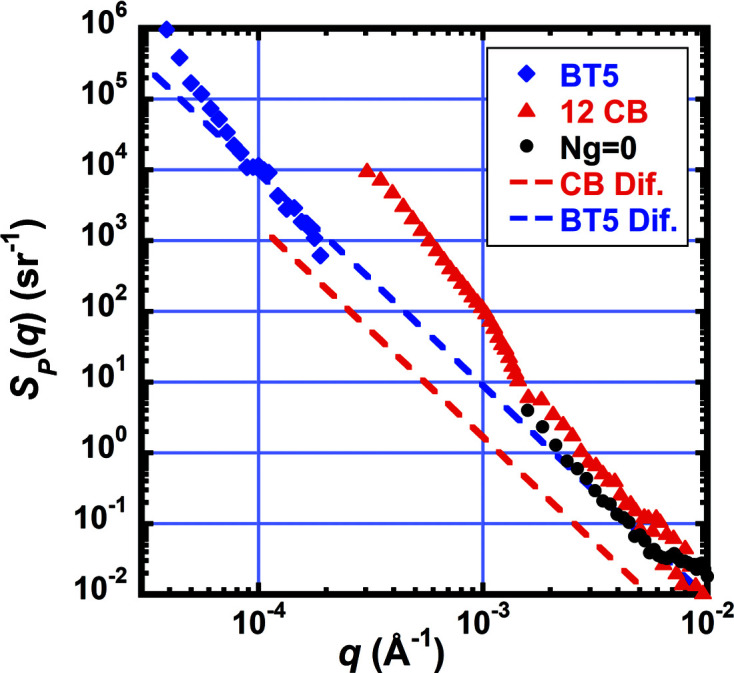
Plot of parasitic background given as a scattering probability versus q from the BT5 USANS instrument (blue) and two different VSANS instrument configurations: (i) 12 CB (red) and (ii) N G = 0 pinhole collimation (black). Dashed lines are the expected diffraction from the corresponding sample apertures. The graph can be used to estimate the required scattering cross section of a sample needed to achieve a desired S/N ratio. For example, to have S/N = 1 at q = 0.001 Å−1, where the noise S(q) is ∼102 sr−1, would require for a d S = 0.1 cm-thick sample the macroscopic cross section dΣ/dΩ = S(q)/d S ≃ 1000 cm−1 sr−1 at q = 0.001 Å−1.
