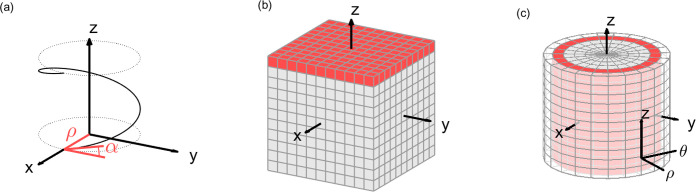
Figure 1.
Illustration of the base geometries used in the proposed method: (a) a helix around the z-axis with radius ρ and inclination angle α; (b) a discrete voxel grid in Cartesian coordinates, where each cube is a voxel; and (c) a discrete voxel grid in cylindrical coordinates, where the voxels are no longer cubes, but trapezoidal prisms. An orthoslice at constant z and a cylindrical section at constant ρ are highlighted in red in b and c, respectively.