Figure 2.
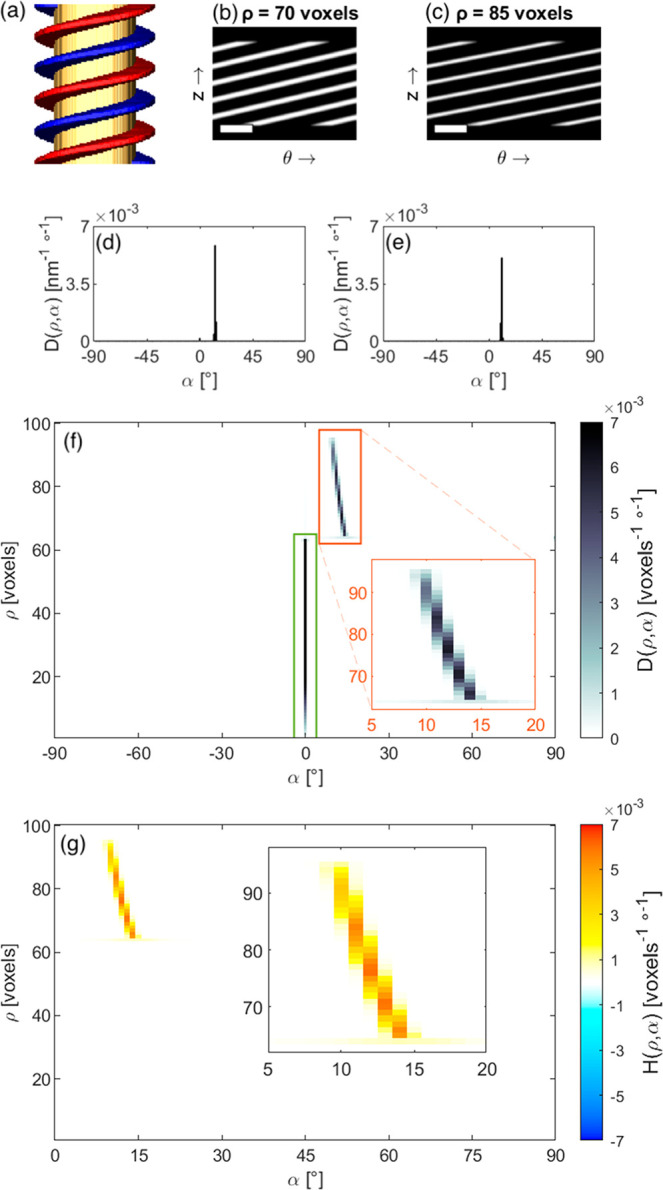
A simulated helix (a) with two of its cylindrical sections at ρ = 70 voxels (b) and ρ = 85 voxels (c). The scale bars are 100 voxels wide. The model consists of an achiral core (yellow) enveloped by two helices (blue and red). The directionality for the two cylindrical sections is shown in d and e, respectively, and the directionality of all cylindrical sections is combined in a histogram (f), to obtain the directionality of the 3D helix in cylindrical coordinates. Two main features in f are marked by green and orange boxes, and the orange region is enlarged in the inset. (g) Helicity function H(ρ,α) histogram and zoomed view (inset) of the peak corresponding to the helical shell of the model. Note that the line is not vertical due to the different angles involved in the model helix.
