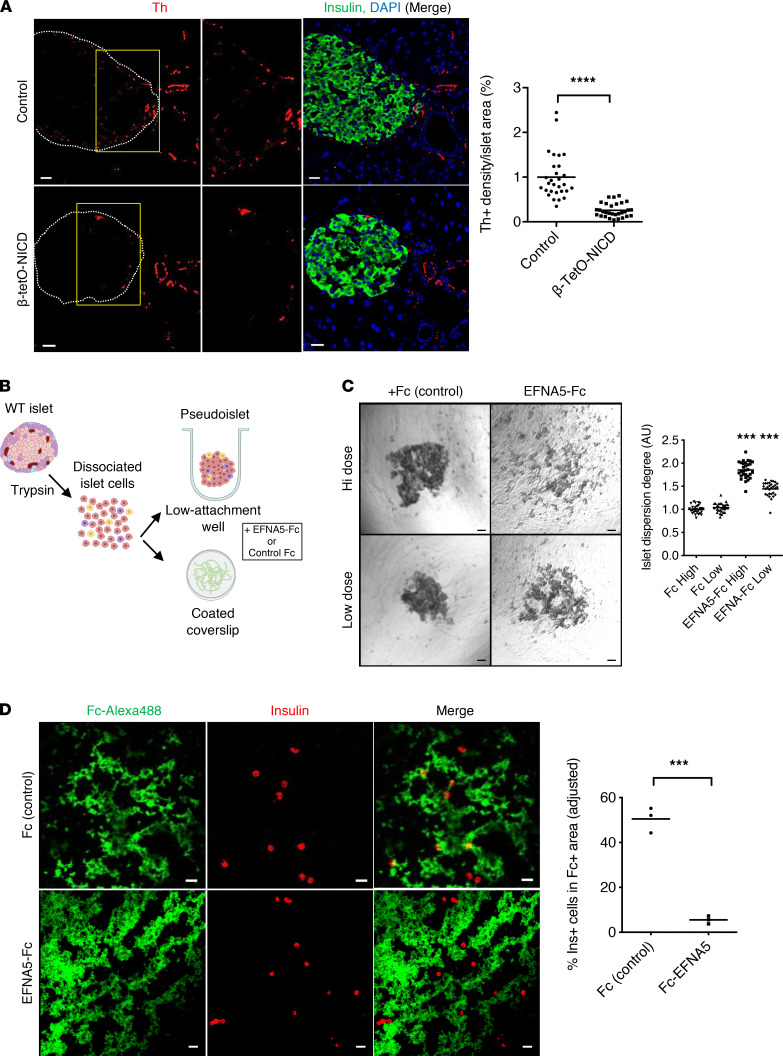
Figure 5. Repulsive effects of EFNA5 on mouse β cells.
(A) Representative images and morphometric analysis of Th-positive area in β-tetO-NICD and Cre– controls after 8 weeks’ Dox. Individual islets from at least 5 mice/group are plotted. (B) Experimental workflow for pseudoislet formation and cell repulsion assays. Islets were dissociated into single cells that were incubated in ultra-low-attachment wells for pseudoislet formation, or applied to coated coverslips for adhesion assays, in the presence of EFNA5-Fc chimera or Fc control. (C) Representative images and quantitation of pseudoislet formation of dispersed islet cells after 4-day exposure to EFNA5-Fc or Fc control, at high (55 nM) or low (13.75 mM) dose. Data pooled from 3 independent experiments. (D) Representative images and quantitation of β cells in EFNA5-Fc–coated condition (normalized to Fc control). Data shown as average of 3 independent experiments. Scale bars: 20 μm. All data are shown with group means; ***, P < 0.001, ****, P < 0.0001 by 2-tailed t test.