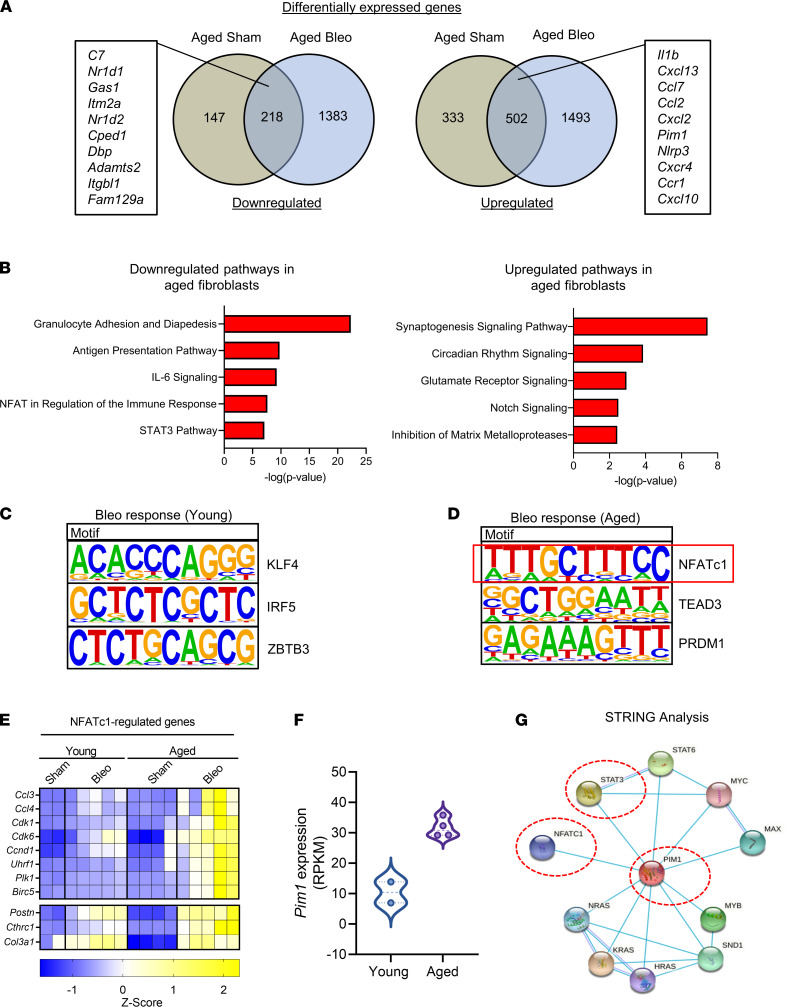
Figure 2. PIM1 and NFATc1 signaling pathways are associated with impaired fibrosis resolution in aged mice after bleomycin injury.
(A) Venn diagrams of differentially regulated genes from uninjured aged and injured aged fibroblasts relative to uninjured young fibroblasts. Intersection genes with the highest average expression are displayed. (B) Ingenuity pathway analysis of the intersection genes identifies differentially regulated canonical pathways. (C) De novo transcription factor binding motif analysis of differentially expressed genes in young fibroblasts after injury showing the top 3 binding motif and their associated transcription factors. (D) De novo transcription factor binding motif analysis of differentially expressed genes in aged lung fibroblasts after injury showing the top 3 binding motif and their associated transcription factor. Red box indicates highest ranked transcription factor binding motif and associated transcription factor in aged lung fibroblasts. (E) Heatmap of genes with NFATc1 binding motifs displayed as Z scores of RPKM (young sham, n = 2; young bleo 30 days, n = 5; aged sham, n = 4; aged bleo 30 days, n = 5). (F) Expression of PIM1 gene in young and aged lung fibroblasts (young sham, n = 2; aged sham, n = 4). (G) STRING functional protein association networks showing an interconnection between PIM1, STAT3, and NFATc1. Each node represents a protein, and each line represents a curated interaction.