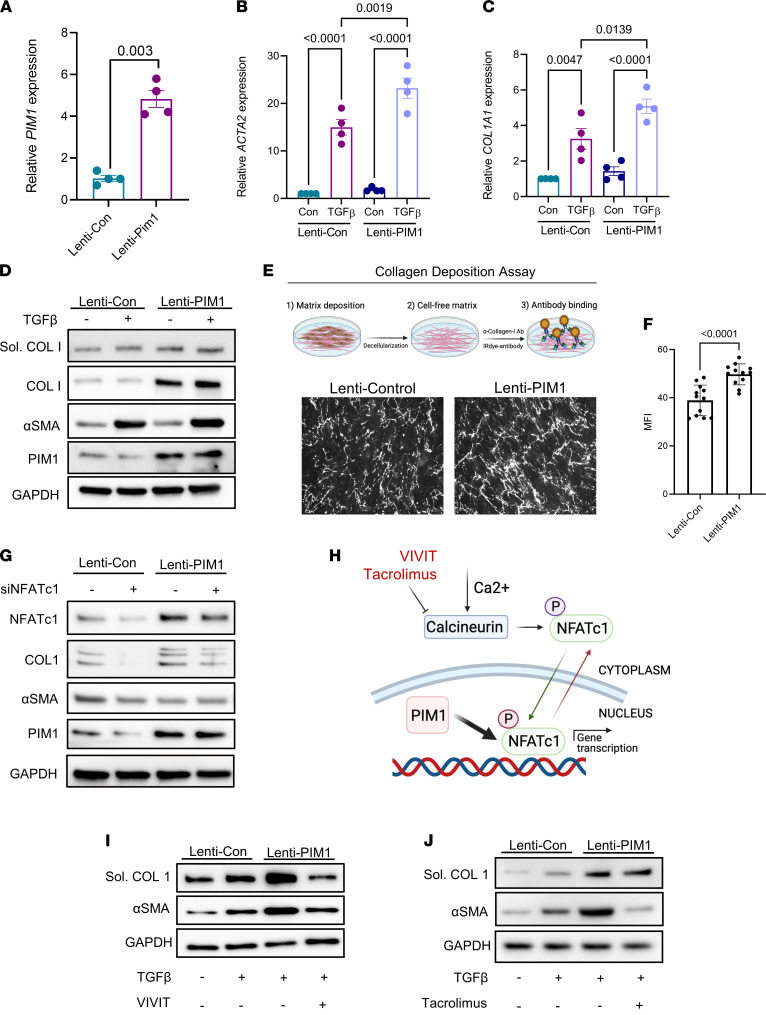
Figure 4. NFATc1 inhibition attenuates PIM1-promoted lung fibroblast activation.
(A) Normal human lung fibroblasts transduced with control lentivirus (pLV-EGFP-CMV-mCherry) or lentivirus carrying the human PIM1 gene (pLV-EGFP-CMV-hPIM1) for 48 hours, followed by FACS to collect GFP+ cells. Shown is the mRNA expression of PIM1 evaluated by qPCR. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of n = 4 independent experiments. P values were calculated using 2-tailed, paired Student’s t test. (B and C) mRNA expression of ACTA2 (B) and COL1A1 (C) in control and PIM1 overexpressing cells treated with 2 ng/mL of TGF-β for 24 hours. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of n = 4 independent experiments. P values were calculated using 1-way ANOVA with Holm-Šidák post hoc test. (D) Normal human lung fibroblasts transduced with control lentivirus or PIM1 lentivirus were treated with 2 ng/mL of TGF-β for 24 and then analyzed by Western blotting. Shown is a representative blot of gels run in parallel. (E) Representative images of collagen-I fibers from a collagen deposition assay carried out in control and PIM1-overexpressing cells. (F) Quantification of collagen-I secretion measured as mean fluorescence intensity. n = 12. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. P values were calculated using 2-tailed Student’s t test. (G) Control and PIM1-overexpressing cells were transfected with scrambled or NFATc1 siRNAs for 48 hours, followed by Western blotting analysis. Shown is a representative blot of 3 independent experiments. (H) Schematic showing mechanisms of NFATc1 inhibition by VIVIT and tacrolimus. Following phosphorylation, NFATc1 is sequestered in the cytoplasm. Upon dephosphorylation by calcineurin, NFATc1 translocates into the nucleus, where it becomes transcriptionally active. In the nucleus, PIM1 can phosphorylate NFATc1 to enhance its transcription. (I and J) Western blotting analysis of control and PIM1 overexpressing lung fibroblasts cotreated with 2 ng/mL of TGF-β and the NFATc1 inhibitors VIVIT (5 μM) and tacrolimus (1 μM). Shown is a representative blot of 3 independent experiments.