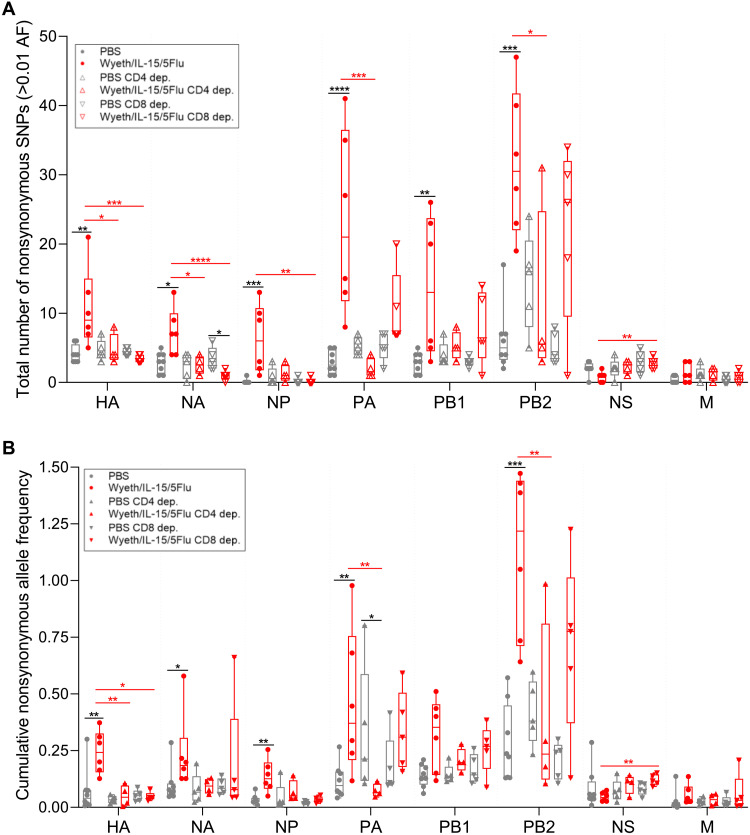
Fig. 4. CD4 and CD8 depletion leads to reduced mutations in Wyeth/IL-15/5Flu–vaccinated mice at day 7 after H1N1 challenge.
(A) Total number of nonsynonymous SNPs and (B) cumulative AF arising in IAV gene sequences isolated from H1N1 day 7 p.i. nondepleted (same sequence data from Fig. 2), CD4+ and CD8+ T cell–depleted BALB/c mice vaccinated with PBS or Wyeth/IL-15/5Flu, across all eight IAV genes (≥0.01 AF). Individual data points shown on box and whisker plots, showing mean and upper and lower quartiles with minimum-maximum range. Statistical significance was determined by a Kruskal-Wallis test. False discovery rate (0.1) was determined by the original Benjamini and Hochberg method. Black annotation denotes significance between different vaccination groups at the same time point; red annotation denotes significance between different depletion status within the same vaccination group. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, and ****P ≤ 0.0001. PCR and sequencing were performed in parallel for the control nondepleted group of day 7 from Fig. 2; therefore, the same nondepleted PBS and Wyeth/IL-15/5Flu control samples were used in Fig. 2 and in this figure.