Figure 4. Impact of Poly-A Particle Phagocytosis on surface protein expression by human neutrophils.
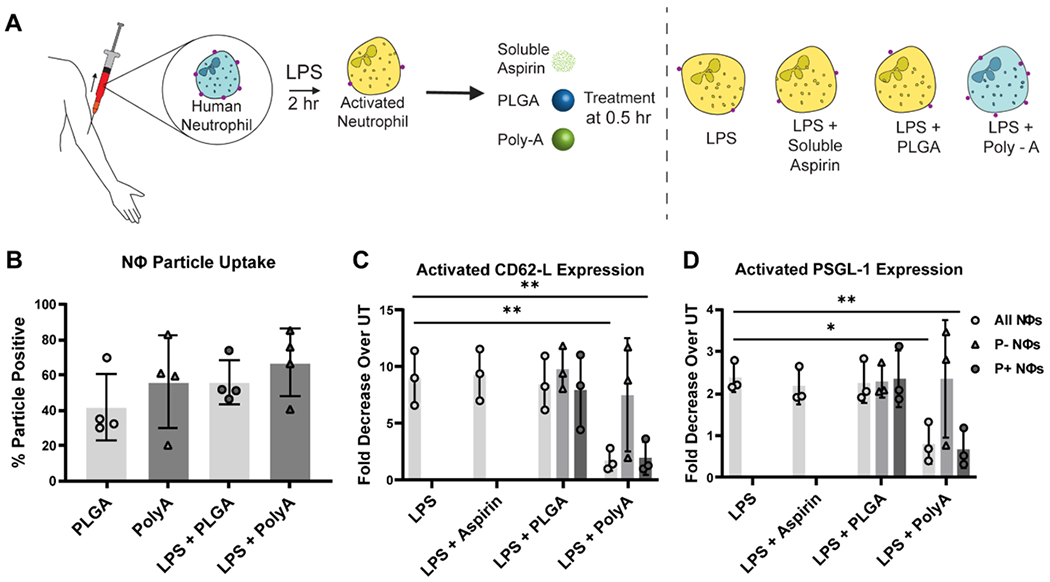
(A) Schematic depiction of L-selectin surface expression (red dots) by neutrophils in naïve or LPS-activated cells with or without particle treatment. (B) The fraction of neutrophils that internalized particles in whole blood. (C) Fold decrease in L-selectin (CD62-L) surface expression by neutrophils in whole blood exposed to LPS only, LPS + Aspirin, LPS + PLGA, and LPS + Poly-A particles relative to neutrophils in untreated (UT), non-LPS activated blood. (D) Fold decrease in PSGL-1. Each 100 μL blood sample received 2 x 106 particles for every particle type 30 min after LPS activation, and the protein expression was evaluated at 2 hr after LPS activation. Three human donors were used for this experiment, n=3. P- Nøs = Particle negative neutrophils; P+ Nøs = Particle positive neutrophils. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism Software using One-Way ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD test with a 95% confidence interval. Asterisks indicate p values of: * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.01. N ≥ 3 for all assays unless otherwise stated.
