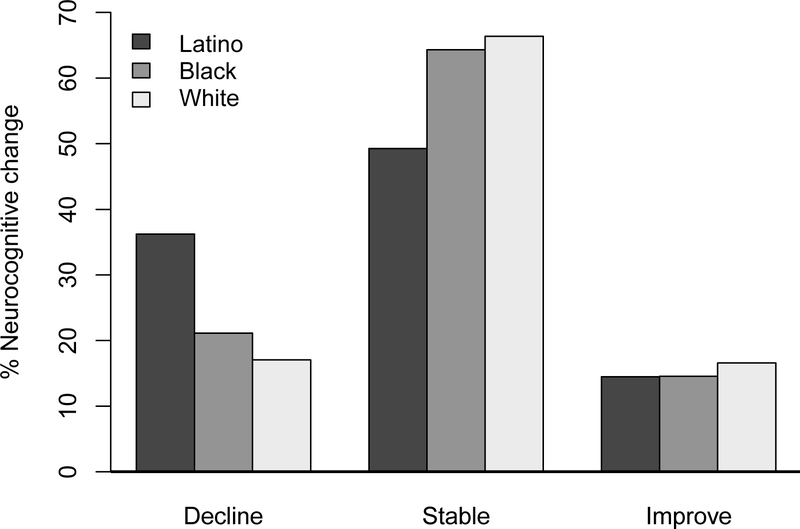
Figure 1.
Neurocognitive change (decline, stable, improve) by ethnicity/race. The overall model showed significant ethnic/racial differences in the proportion of participants who declined, remained stable, or improved neurocognitively (χ2 = 11.84, df = 4, p = 0.019). Latino PWH were at higher risk of neurocognitive decline compared to White (χ2 = 10.24, df = 1, p = 0.001) and Black (χ2 = 5.59, df = 1, p = 0.018) PWH, while Black and White PWH did not differ (χ2 = 0.91, df = 1, p = 0.34).