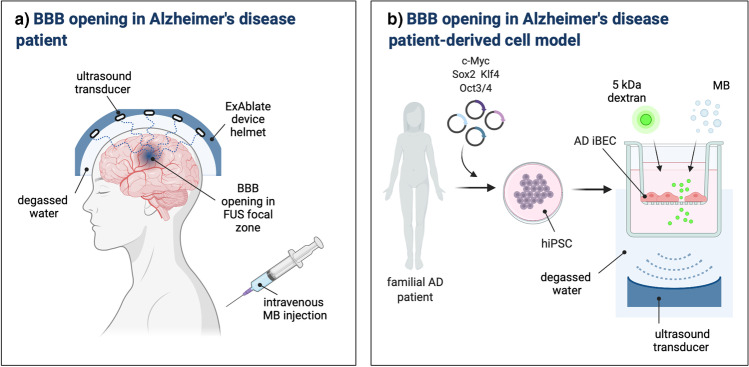
Fig. 3.
Schematic representation of blood-brain barrier opening in Alzheimer’s disease patient in vivo and patient-derived model in vitro. (a) Schematic of a magnetic resonance (MR)-guided ExAblate device used in the first successful blood-brain barrier (BBB) opening in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients. System consists of a hemispherical helmet lined with >1000 independent transducer elements delivering low frequency ultrasound treatment to the prescribed target. The helmet is positioned in the specialised MRI bed with stereotaxic frame and the space between patient’s head and the helmet filled with degassed water for acoustic coupling. Microbubble (MB) administration is carried out using repeated bolus injection or a continuous infusion. Reversible BBB opening occurs in the defined ultrasound focal zone. (b) Schematic of AD patient-derived human BBB opening in vitro. Somatic cells (e.g. fibroblasts or blood cells) are obtained from familial AD patients and reprogrammed to human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) by introduction of cocktail of reprogramming factors. hiPSC are used to generate brain endothelial-like cells (iBEC) and develop patient-derived in vitro AD BBB model. In vitro BBB is exposed to focused ultrasound and MB in the degassed water, leading to BBB opening and improved permeability of 5 kDa dextran. [44, 84]. AD-Alzheimer’s disease; BBB-blood-brain barrier; FUS-focused ultrasound; hiPSC-human induced pluripotent stem cell; iBEC- brain endothelial-like cells; kDa-kilodalton; MB-microbubble; Figure created with BioRender.com.