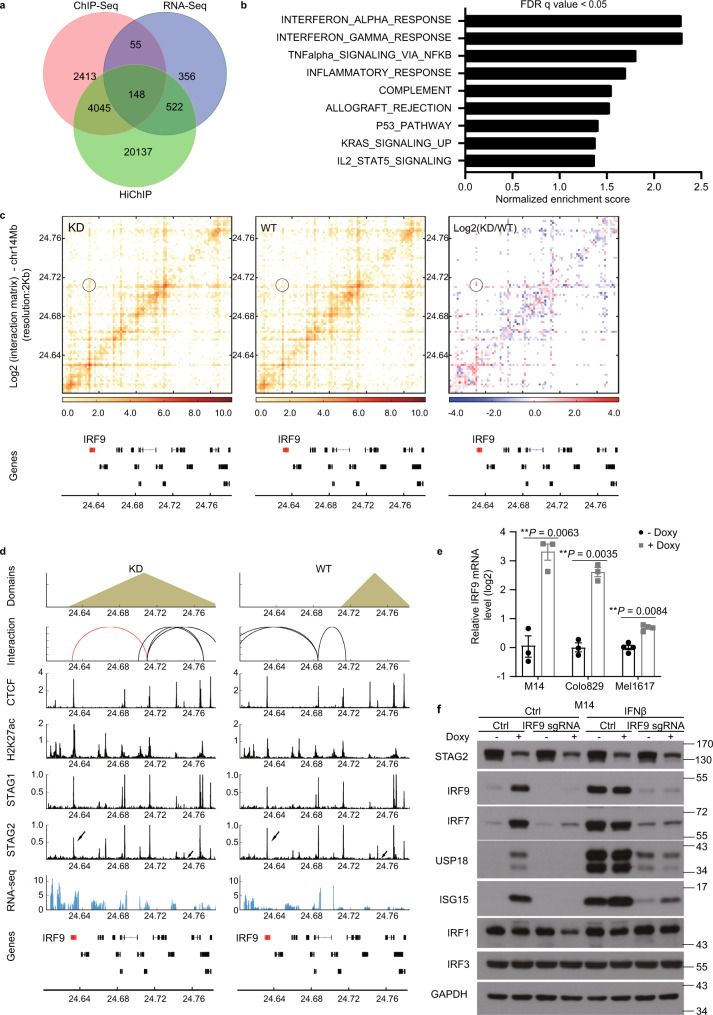
Fig. 3. IRF9 is a key direct target of STAG2 in melanoma.
a Venn diagram illustrates targets of STAG2 identified through integrated H3K27ac HiChIP, RNA-seq, and STAG2 ChIP-seq analyses in M14 cells. b GSEA of RNA-seq data (n = 3) reveals enriched pathways induced by STAG2 KD in M14 cells. c STAG2 knockdown led to the formation of a new H3K27ac-associated interaction between IRF9 promoter and a distal enhancer, as revealed in H3K27ac HiChIP analysis (n = 2). d Hi-C, H3K27ac HiChIP, ChIP-seq, and RNA-seq profiles at the IRF9 locus in M14 cells with (KD) and without (WT) STAG2 knockdown. An H3K27ac-associated loop anchored at the IRF9 promoter is highlighted in red. e qPCR analysis of IRF9 mRNA levels in human melanoma cell line M14 (n = 3), Colo829 (n = 3), and Mel1617 (n = 4) with doxy-inducible STAG2 shRNA. Data were presented as mean ± SEM. Two-tailed ratio paired t-tests, **P < 0.01. f M14 cells with doxy-inducible STAG2 shRNA were transfected with ctrl or IRF9 sgRNA. Cells were cultured in the presence or absence of doxycycline for 5 days and stimulated with or without IFNβ (500U/ml) for 24 h before lysates were used for immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. (n = 3). For all panels, n values indicate the number of biologically independent samples.