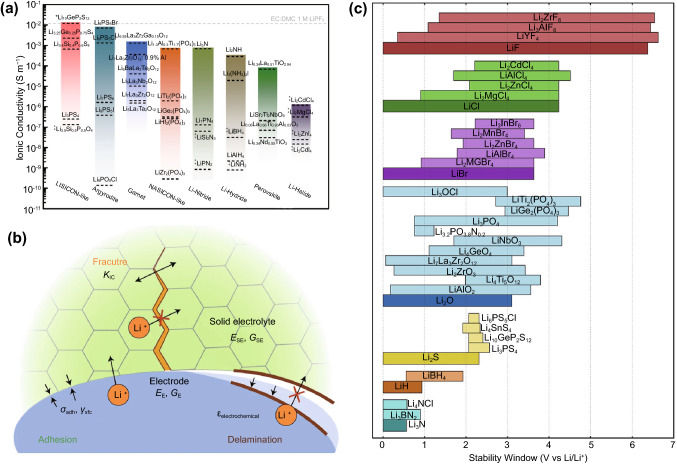
Fig. 16.
a Lithium ionic conductivity of selected inorganic solid electrolytes and a comparison to a typical organic liquid electrolyte [227].
Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society. b Various inorganic solid electrolyte damage mechanisms that can occur as a result of cycling [232]. Copyright 2015, American Chemical Society. c The electrochemical stability window of some inorganic solid state lithium-ion conductors grouped by the anion type, along with the typically more stable but non-conducting binary compounds [233]. Copyright 2019, Springer Nature