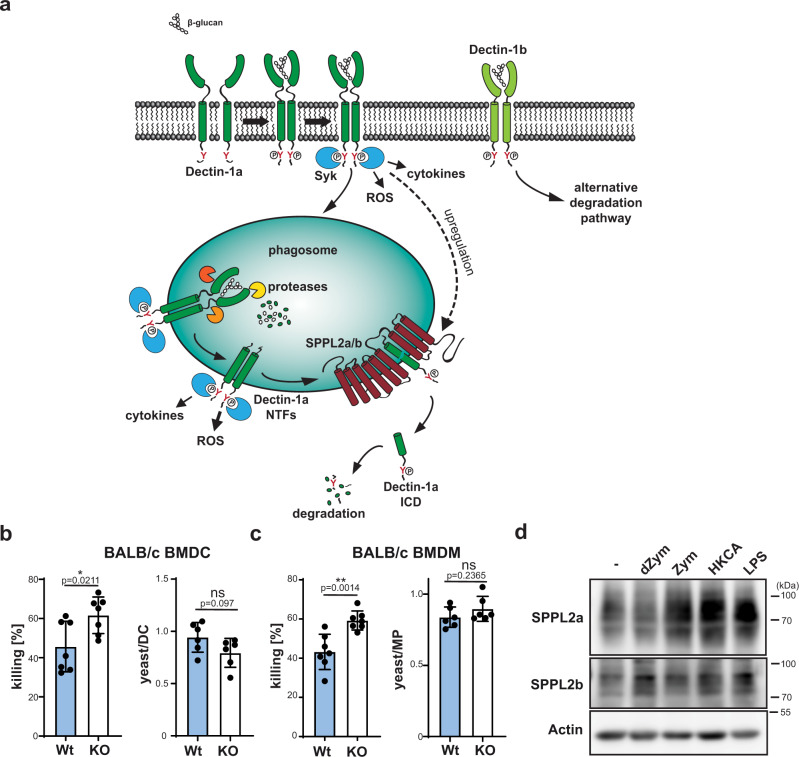
Fig. 7. SPPL2 proteases regulate killing of C. albicans yeasts as part of a regulatory circuit.
a Schematic overview of differential processing of Dectin-1 isoforms. Upon ligand binding, Dectin-1a is phosphorylated at the intracellular hemITAM (red Y) leading to the recruitment of kinases including Syk as well as the induction of downstream responses including the formation of ROS and the induction of cytokine secretion. Additionally, ligand binding enforces internalisation of Dectin-1a into phagosomes where it is processed by soluble proteases to a membrane-embedded Dectin-1a NTF. This fragment is still capable of transmitting signalling responses and requires SPPL2a/b for its degradation and termination of Dectin-1a-dependent signal transduction. Dectin-1b utilises alternative degradative pathways. b Killing as well as phagocytosis of C. albicans yeasts (MOI 1) was assessed for BMDC from either wild type (Wt) or SPPL2b−/− mice (2b KO) mice on BALB/c background. Killing: N = 3, n = 7; phagocytosis N = 2, n = 6. Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. c The same was done for BMDM derived from the same mice. Killing: N = 3, n = 7; phagocytosis N = 2, n = 6. Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. d BMDCs from BALB/c wild-type mice were treated for 24 h with either 50 µg/ml dZym, 50 µg/ml Zym, MOI 10 HKCA or 500 ng/ml LPS and finally monitored for SPPL2a/b protein abundance by western blotting employing specific antibodies against the proteases. N = 4, n = 4. All diagrams depict Mean values ± SD.