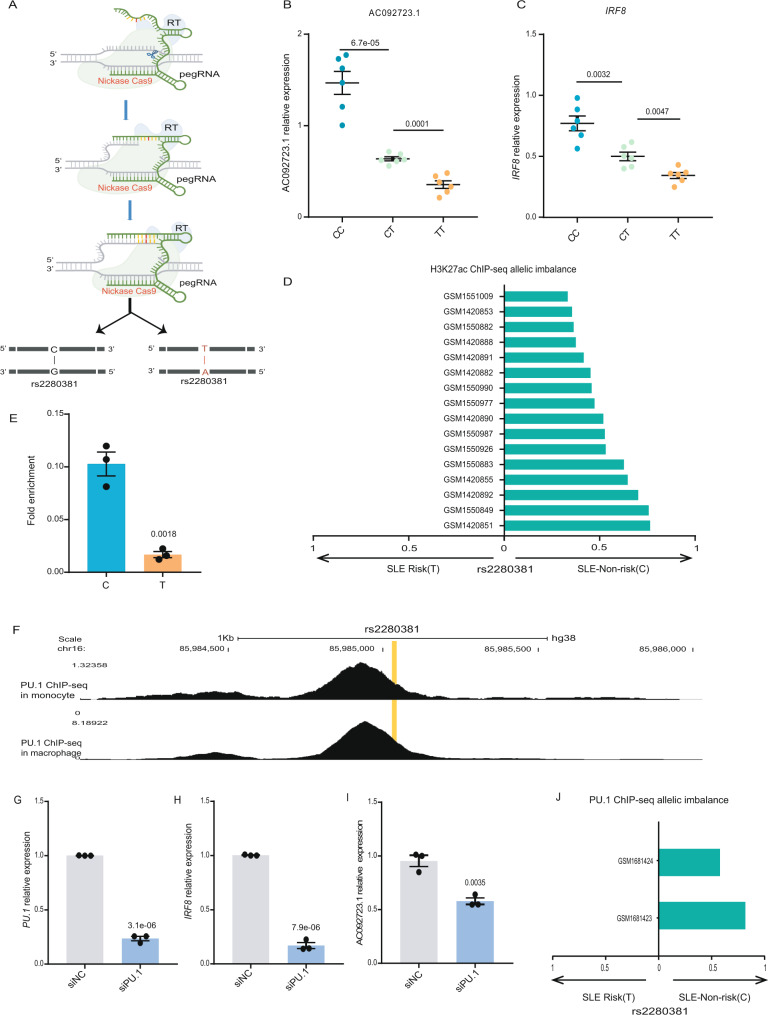
Fig. 5. rs2280381 alleles affect H3K27ac and PU.1 binding to fine-tune the expression of AC092723.1 and IRF8.
A Workflow for the generation of isogenic cell clones with the Prime editing technology. RT Reverse Transcriptase. B, C The rs2280381 C allele leads to higher expression of AC092723.1 and IRF8 compared to the T allele. (n = 6, biologically independent samples). D Genotype-dependent binding of H3K27ac for rs2280381. Results with MARIO ARS value >0.4 across ChIP-seq datasets are included. The X-axis indicates the preferred allele, along with a value indicating the strength of the allelic behavior, calculated as one minus the ratio of the weak to strong read counts (e.g., 0.5 indicates the strong allele has twice the reads of the weak allele). ARS allelic reproducibility score. E The genomic region containing the non-risk allele C exhibits increased chromatin accessibility compared to the risk allele T, as determined by AS-FAIRE-qPCR in the rs2280381 heterozygous U-937 cell clone. (n = 3, biologically independent experiments). F ChIP-seq in monocyte and macrophage indicates the PU.1 binds to rs2280381 site. Relative expression of PU.1 (G), IRF8 (H) and AC092723.1 (I) after PU.1 siRNA-mediated knockdown, as measured by RT-qPCR in primary monocytes (n = 3, biologically independent experiments). J PU.1 prefers binding to the rs2280381 C non-risk allele, as analyzed by MARIO methods using the PU.1 ChIP-seq data in primary monocytes or macrophage provided by ADASTRA database. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, and p values are calculated using an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test. ns not significant. See also Supplementary Fig. 8.