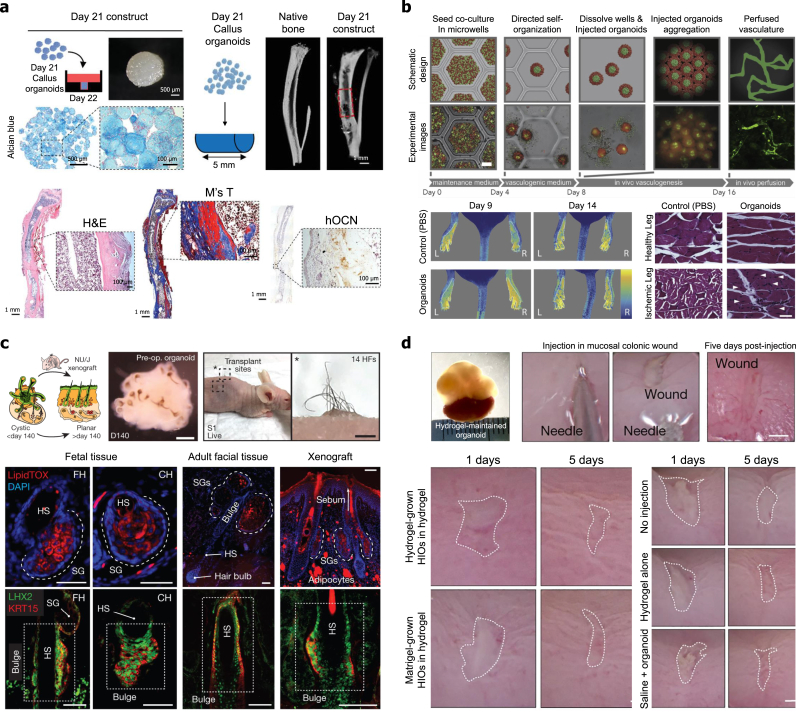
Fig. 6.
Therapeutic applications of stem cell-induced organoids for regeneration of tissue and restoration of organ function. (a) Bone tissue repair and regeneration using human periosteum-derived stem cells-derived multiple callus organoids developed by agarose microwell. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [236]. Callus organoids were assembled to form larger constructs in agarose well. Assembled callus organoids enhanced regeneration of critical-sized long bone defects. (b) Blood vessel and muscle tissue repair and regeneration using vascularized organoids. Mouse MSCs and HUVECs-derived vascularized organoids developed by sacrificial alginate microwells. Prevascularized organoids regained perfusion of the ischemic limb, had more viable myofibers, and exhibited regenerating myofibers. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [134]. (c) Skin tissue repair and regeneration using cyst-like skin organoids. Cyst-like skin organoids derived from human ESCs were used for reconstructing appendage-bearing skin tissue. The developed organoids enhanced the formation of planar hair-bearing skin, including hair follicles and sweat glands. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [60]. (d) Intestinal tissue repair and regeneration using intestinal organoids. Intestinal organoids generated by encapsulation of hPSCs into a synthetic four-armed maleimide-terminated PEG hydrogel. The matured organoids improved the mucosal colonic wound closure. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [228].