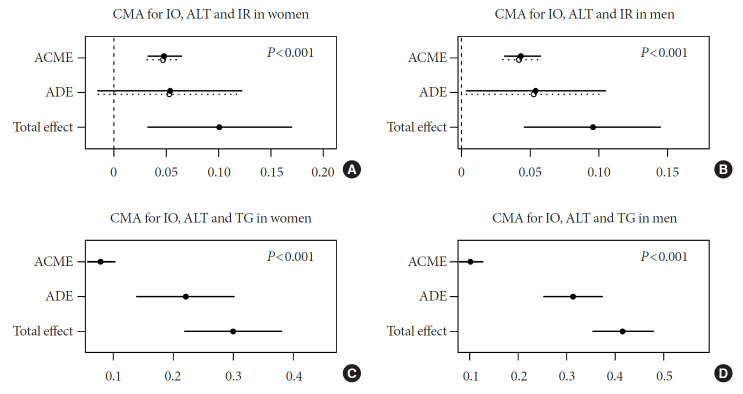
Fig. 1.
Causal mediation analysis (CMA) models for the association of insulin resistance (IR) and triglyceride (TG) metabolism with iron overload (IO). Adjusted for age and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. (A, B) The circles and solid lines show the point estimates and 95% confidence intervals for the effects of IO on IR and (C, D) TG metabolism. (A, B) The average causal mediation effects (ACMEs) reflect the indirect effects of IO on IR and (C, D) TG metabolism, mediated by alanine aminotransferase. (A, B) The average direct effects (ADEs) reflect the direct effects of IO on IR and (C, D) TG metabolism. The total effects are equal to ACME plus ADE. P indirect represents the P value for ACME.