Fig. 1.
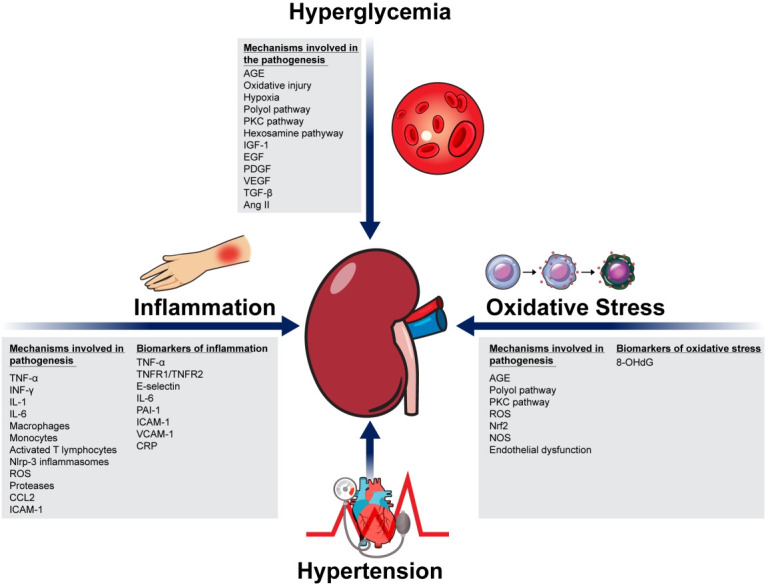
The pathophysiology of potential and novel biomarkers of diabetic kidney disease classified by their target pathophysiological pathways. AGE, advanced glycation end products; PKC, protein kinase C; IGF-1, insulin like growth factor-1; EGF, epidermal growth factor; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; Ang II, angiotensin II; TNF-α, tissue necrosis factor-α; INF-γ, interferon-γ; IL-1, interleukin-1; IL-6, interleukin-6; Nlrp3, nod-like receptor protein-3; ROS, reactive oxygen species; CCL2, C-C motif chemokine 2; ICAM-1, intracellular adhesion molecule 1; TNFR1, tissue necrosis factor receptor 1; TNFR2, tissue necrosis factor receptor 2; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion protein-1; CRP, C-reactive protein; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; 8-OHdG, 8-Hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine.
