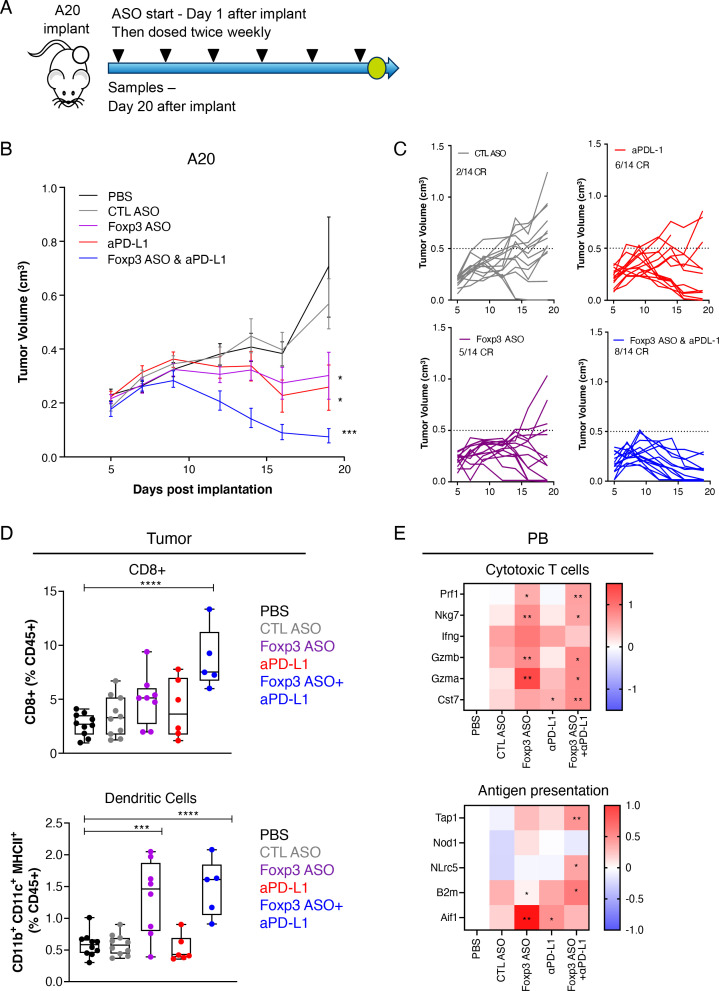
Figure 5.
FOXP3 ASOs promote antitumor efficacy when combined with αPD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade. (A) Mice were treated with mouse FOXP3 ASO (895317) (50 mg/kg BIW) and αPD-L1 (10 mg/kg BIW) alone or in combination from day 1 post A20 tumor-implantation and dosed two times per week for the duration of the experiment. N=14 per group. (B) Mean tumor and (C) individual tumor volumes and indicated number of complete responses (CR). (D-E) Tumor samples and peripheral blood (PB) were analyzed at day 20 by flow cytometry and RNA levels, respectively. (D) Frequency of CD8 +T cells and dendritic cells in tumor and (E) cytotoxic T cell and antigen-presenting cell gene markers in PB. *, P≤0.05; **, p≤0.01; ***, p≤0.001; ****, p≤0.0001 by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s post-test for (D and E) and two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test for (B). Differences are calculated relative to PBS. ASOs, antisense oligonucleotides; BIW, two times per week; PBS, phosphate buffered saline; PD-1, programmed cell death 1; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand 1.