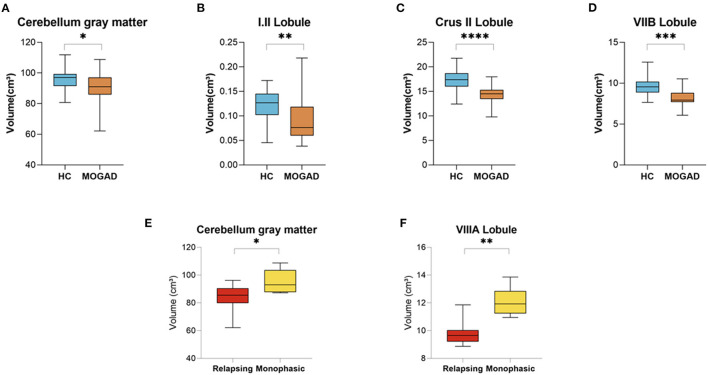
Figure 5.
Decrease volume of cerebellar lobules at MOGAD patients compared to HCs and decreased volume of cerebellar lobules at relapsing MOGAD patients compared to monophasic MOGAD patients. (A–D) Volume of cerebellar lobules of HCs (n = 22) and MOGAD patients (n = 20) analyzed by CERES pipeline of Volbrain software. Volume of (A) total cerebellum gray matter (96.23 ± 6.89 vs. 90.66 ± 10.43, p = 0.050), (B) cerebellar lobules I.II (0.12 ± 0.03 vs. 0.09 ± 0.05, p = 0.009), (C) Crus II (17.33 ± 2.18 vs. 14.39 ± 1.75, p < 0.001), and (D) VIIB (9.70 ± 1.24 vs. 8.26 ± 1.09, p < 0.001) of MOGAD patients and HCs. (E,F) Volume of cerebellar lobules of monophasic (n = 6) and relapsing (n = 6) MOGAD patients analyzed by CERES pipeline of Volbrain software. Volume of (E) total cerebellum gray matter (83.14 ± 10.78 vs. 95.34 ± 8.52, p = 0.047) and (F) cerebellar lobule VIIIA (9.87 ± 0.97 vs. 12.09 ± 1.03, p = 0.002) of monophasic and relapsing MOGAD patients. MOGAD, Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody disorders; HCs, healthy controls. p * ≤ 0.05, ** ≤ 0.01, *** ≤ 0.001, **** ≤ 0.0001.