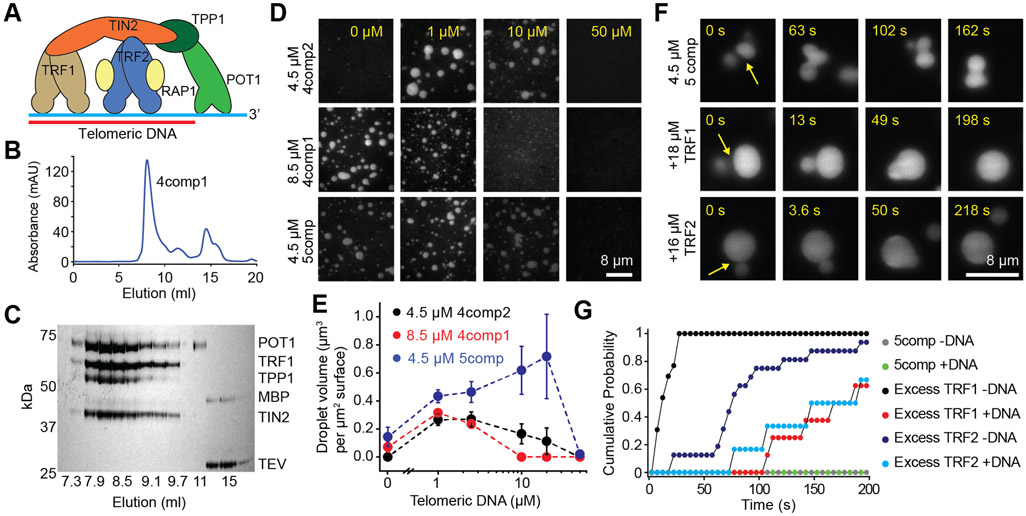
Figure 4. The shelterin complex phase separates in vitro.
A. A schematic of the human shelterin complex. TRF1 and TRF2 are homodimers that bind to dsTEL, and POT1/TPP1 binds to ssTEL. TIN2 interconnects TRF1, TRF2, and TPP1, and RAP1 binds to TRF2. B-C. UV absorbance (B) and denaturing gel (C) show that 4comp1 elutes as a single complex from a gel filtration column. D. 4comp2 and 5comp exhibit reentrant responses to increasing DNA concentration similar to TRF2 droplets, while 4comp1 is inhibited by increasing DNA concentration similar to TRF1 droplets. E. The total volume of shelterin droplets settled per micron squared area on the coverslip under variable 8ds3ss concentration (mean ± SD, n = 20 with two technical replicates). F. In the presence of 2.5 μM 8ds3ss, 5comp droplets do not fuse on relevant time scales, whereas the addition of excess TRF1 or TRF2 reduces the fusion time. G. Cumulative probability of 5comp droplet fusion in the presence and absence of excess TRF1 or TRF2 after forming a contact at t = 0 s (n = 7, 4, 13, 16, 15 and 7 events from top to bottom). See also Figure S4 and Movie S4.