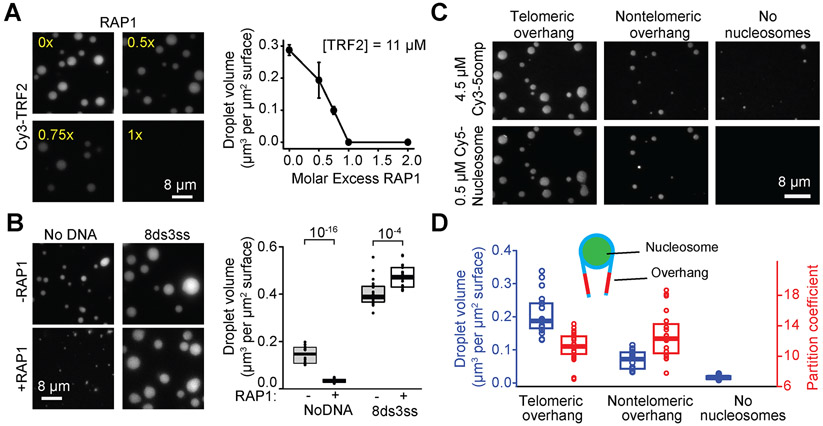
Figure 6. Telomere-associated proteins modulate phase separation of shelterin droplets.
A. (Left) Increasing the molar ratio of RAP1 inhibits phase separation of TRF2 droplets. Droplets were formed in the presence of 2.5 μM 8ds3ss DNA. (Right) The total volume of TRF2 condensates settled per micron squared area on the coverslip as a function of RAP1 concentration (mean ± SD, n = 20 with two technical replicates). B. (Left) 5comp droplets formed with or without equimolar RAP1 and in the presence or absence of 2.5 μM 8ds3ss DNA. Complex concentration was set at 4.5 μM. (Right) The total volume of shelterin condensates settled per micron squared area on the coverslip in the absence or presence of RAP1. The center and edges of the box represent the median with the first and third quartile (n = 20 with two technical replicates). The p-values were calculated from a two-tailed t-test. C. Example images show phase separation of 4.5 μM 5comp in the presence and absence of nucleosomes wrapped with telomeric or nontelomeric DNA. D. Volume of droplets settled per micron squared area and partition coefficient of nucleosomes into 5comp droplets. The center and edges of the box represent the median with the first and third quartiles (n = 20 droplets with two technical replicates). See also Figure S6.