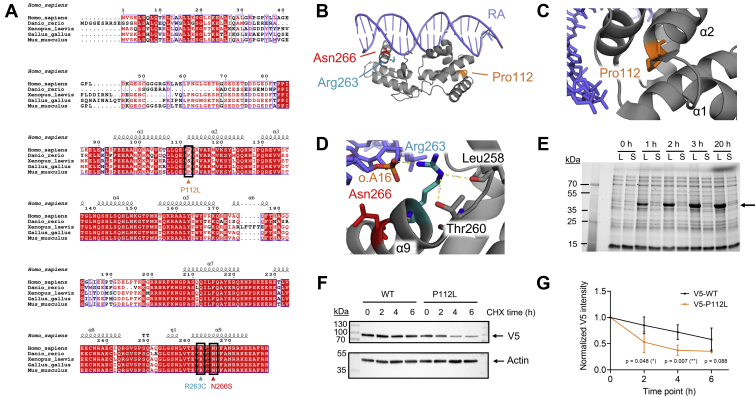
Figure 3.
Overview of the studied variants and protein turnover dynamics of HNF-1A P112L.A, multiple sequence alignment of HNF-1A sequences from model organisms, with variants of interest indicated by black boxes and arrows. B, crystal structure of RA-bound DBD (PDB ID: 1IC8) with mutation sites highlighted. C, magnified view on Pro112 and arrangement of neighboring residues. D, magnified view on Arg263 and Asn266. o.A16 and neighboring residues Leu258 and Thr260 are indicated. E, expression and solubility test for DD-DBD P112L (31.2 kDa) in Escherichia coli Rosetta(DE3). Lysate (L) and soluble fraction (S) at different time points of expression (1–3 h: 37 °C, 20 h: 20 °C, 0 h: uninduced control). Arrow indicates over-expressed protein band with an apparent slow migration behavior, as observed for DD-DBD WT. F, representative Western blot membranes of CHX chase assay analysis of full-length WT and P112L protein turnover. Western blot membranes from all four conducted replicates are shown in Fig. S2. G, quantification of CHX chase assay for HNF-1A WT and P112L, based on normalization to whole protein amount from stain-free SDS-PAGE gel (N = 4, Fig. S2). CHX, cycloheximide; DBD, DNA-binding domain; DD, dimerization domain; HNF-1A, hepatocyte nuclear factor 1A; RA, rat albumin promoter oligonucleotide.