Figure EV1. Molecular aberrations in 55 pediatric high‐risk cancers.
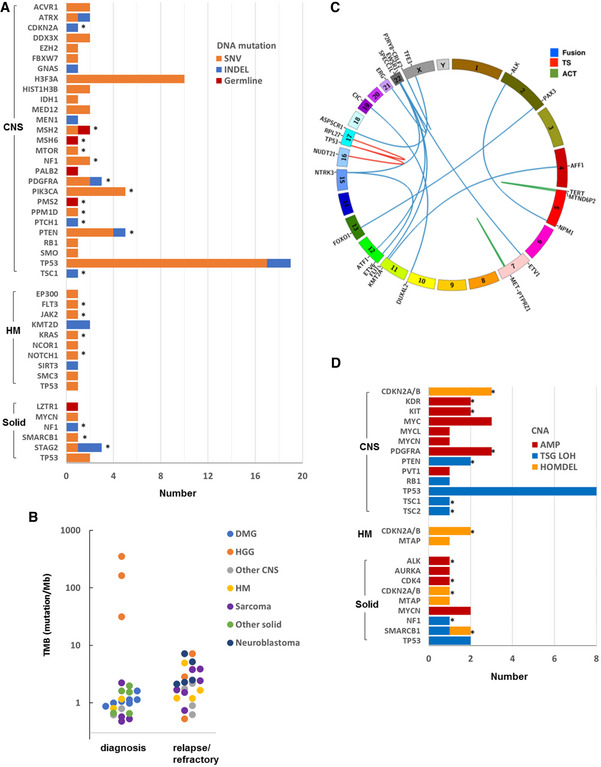
- Genes with somatic and germline DNA mutations (single‐nucleotide variant (SNV) and indel) considered to be pathogenic or likely pathogenic by whole genome sequencing (WGS) and/or panel sequencing. Thirty of 55 samples were found to have 1 or more pathogenic or likely pathogenic mutations. The cohort consists of 27 central nervous system (CNS) tumors, 8 hematologic malignancies (HMs), and 20 non‐CNS solid tumors. Targetable aberrations are indicated by asterisks.
- Tumor mutation burden (TMB) derived from WGS in 23 samples obtained at diagnosis and 24 samples at refractory/relapse.
- Structural variants (SVs) detected by WGS and/or RNA‐seq in 55 samples. Seventeen reportable SVs included 13 fusions, 2 oncogenic activating (ACT) SVs, and 2 tumor suppressor (TS) loss‐of‐function SV.
- Reportable copy number variations (CNVs) included amplifications (≥ 6 copies), loss of heterozygosity (LOH) associated with a loss‐of‐function mutation in a tumor suppressor gene (TSG LOH) and homozygous deletion (HOMDEL) of TSG. Twenty‐four samples were found to have 1 or more reportable CNV. Targetable aberrations are indicated by asterisks.
