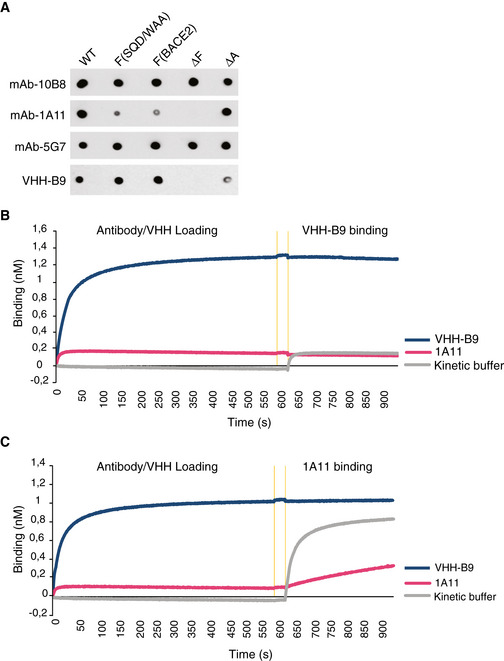
VHH‐B9 binds to a unique exosite on BACE1. Wild‐type (WT) BACE1 ectodomain (1–460) or various mutants, including S376Q377D378/WAA (F(SQD/WAAA)), EDVATSQDD371‐379/MGAGLNYE (F(BACE2)), EVATSQD371‐378/EGS (ΔF), and GFPLNQSEVLASVG219‐232/GAG (ΔA), were purified from cultures of HEK293 cells. 200 ng purified protein was dotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane and probed with the indicated antibodies. Monoclonal antibodies 10B8, 5G7, and 1A11 were used as positive controls. 10B8 and 5G7 recognize all forms of BACE1 tested, indicating that the mutants were properly folded. 1A11 does not recognize BACE1 with mutations in loop F but recognizes Helix A mutants, as well as WT BACE1, as previously reported (Zhou
et al,
2011). VHH‐B9 only weakly recognized ΔLoop F and ΔHelix A mutants, but recognized other Loop F mutants, S376Q377D378/WAA and EDVATSQDD371‐379/MGAGLNYE. Helix A is a structure adjacent to Loop F, flanking the active‐site cleft of BACE1. This suggests that VHH‐B9 binds via a conformational epitope engaging Helix A and Loop F, although direct binding to Loop F may not necessarily be needed. Binding to these structural elements, unique to BACE1, likely explains the specific inhibition seen with VHH‐B9.